Abstract.
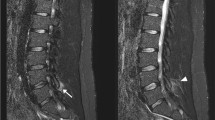
Lumbosacral epidural lipomatosis (LEL) is characterized by excessive deposition of epidural fat (EF). The purpose of our retrospective study was to quantify normal and pathologic amounts of EF in order to develop a reproducible MRI grading of LEL. In this study of 2528 patients (1095 men and 1433 women; age range 18–84 years, mean age 47.3 years) we performed a retrospective analysis of MRI exams. We obtained four linear measurements at the axial plane parallel and tangent to the superior end plate of S1 vertebral body: antero-posterior diameter of dural sac (A-Pd DuS), A-Pd of EF, located ventrally and dorsally to the DuS, and A-Pd of the spinal canal (Spi C). We calculated (a) DuS/EF index and (b) EF/Spi C index. We developed the following MRI grading of LEL: normal, grade 0: DuS/EF index ≥1.5, EF/Spi C index ≤40%; LEL grade I: DuS/EF index 1.49–1, EF/Spi C index 41–50% (mild EF overgrowth); LEL grade II: DuS/EF index 0.99–0.34, EF/Spi C index 51–74% (moderate EF overgrowth); LEL grade III: DuS/EF index ≤0.33, EF/Spi C index ≥75% (severe EF overgrowth). The MRI exams were evaluated independently by three readers. Intra- and interobserver reliabilities were obtained by calculating Kappa statistics. The MRI grading showed the following distribution: grade 0, 2003 patients (79.2%); LEL grade I, 308 patients (12.2%); LEL grade II, 165 patients (6.5%); and LEL grade III, 52 patients (2.1%). The kappa coefficients for intra- and interobserver agreement in a four-grade classification system were substantial to excellent: intraobserver, kappa range 0.79 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.65–0.93] to 0.82 (95% CI, 0.70–0.95); interobserver, kappa range 0.76 (95% CI, 0.62–0.91) to 0.85 (95% CI, 0.73–0.97). In LEL grade I, there were no symptomatic cases due to fat hypertrophy. LEL grade II was symptomatic in only 24 cases (14.5%). In LEL grade III, all cases were symptomatic. A subgroup of 22 patients (42.3%) showed other substantial spinal pathologies (e.g., disk herniation). By means of simple reproducible measurements and indexes MRI grading enables a distinction between mild, moderate, and severe EF hypertrophy. Kappa statistics indicate that LEL can be reliably classified into a four-grade system by experienced observers.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roy-Camille R, Mazel C, Husson J, Saillant G (1991) Symptomatic spinal epidural lipomatosis induced by long-term steroid treatment. Spine 16:1365–1371
Koch C, Doppman J, Watson J, Patronas N, Neiman L (1999) Spinal epidural lipomatosis in a patient with the ectopic corticotropin syndrome. N Engl J Med 341:1399–1400
Gero B, Chynn K (1989) Symptomatic spinal epidural lipomatosis without exogenous steroid intake. Report of a case with MRI. Neuroradiology 31:190–192
Fessler R, Johnson D, Brown F, Erickson R, Reid S, Kranzler L (1992) Epidural lipomatosis in steroid-treated patients. Spine 17:183–188
Kumar K, Nath R, Tchng S (1996) Symptomatic epidural lipomatosis secondary to obesity. J Neurosurg 85:348–350
Frank E (1998) Endoscopic suction decompression of idiopathic epidural lipomatosis. Surg Neurol 50:333–335
Haddad S, Hitchon P, Godersky J (1991) Idiopathic and glucocorticoid-induced spinal epidural lipomatosis. J Neurosurg 74:38–42
Borstlap A, Van Rooij W, Sluzewski M, Leyten A, Beute G (1995) Reversibility of lumbar epidural lipomatosis in obese patients after weight-reduction diet. Neuroradiology 37:670–673
Sato M, Yamashita K, Aoki Y, Hiroshima K (1995) Idiopathic spinal epidural lipomatosis. Case report and review of the literature. Clin Orthop 320:129–134
Soloniuk D, Pecoraro S, Munschauer F (1989) Myelopathy secondary to spinal epidural lipomatosis. A case report. Spine 14:119–122
Evison G, Windsor P, Duck F (1979) Myelographic features of the normal sacral sac. Br J Radiol 52:777–779
Hierholzer J, Benndorf G, Lehmann T, Schneider G, Podrabsky P, Sander B et al. (1996) Epidural lipomatosis: case report and literature review. Neuroradiology 38:343–348
Levy-Weil FE, Feldmann JL (2000) Epidural lipomatosis. Presse Med 29:469–475
Schönstöm N, Bolender N, Spengler D (1985) The pathomorphology of spinal stenosis as seen on CT scans of the lumbar spine. Spine 10:806–811
Beaujeux R, Dietemann J, Allal R, Wolfram-Gabel R (1995) Posterior epidural adipose tissue and the narrow lumbar canal: replacement tissue or cause of impingement? J Neuroradiol 22:63–70
Kuhn M, Youssef H, Swan T, Swenson L (1994) Lumbar epidural lipomatosis: the "Y" sign of thecal sac compression. Comput Med Imaging Graph 18:367–372
Baron RB (1989) Nutritional disorder. In: Schroeder SA, Krupp MA, Tierney LM et al. (eds) Current medical diagnosis and treatment. Appleton and Lange, East Norwalk, Connecticut, pp 834–839
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Wolfram-Gabel R, Beaujeux R, Fabre M (1996) Histologic characteristics of posterior lumbar epidural fatty tissue. J Neuroradiol 23:19–25
Robertson S, Vincent C, Traynelis M, Follet K, Menezes A (1997) Idiopathic spinal epidural lipomatosis. Neurosurgery 41:68–75
Daniel M, Doyon D, Bekkali F, Delvalle A, Francke J (1992) MRI of normal spinal epidural fat. J Radiol 73:695–698
Grayling M, Jardine D, McClintock A, Spar J, Witton G (2000) Symptomatic epidural lipomatosis following cyproterone acetate. Aust NZ J Surg 70:233–235
Willén J, Danielson B, Gaulitz A, Niklason T, Schönström N, Hansson T (1997) Dynamic effects on the lumbar spinal canal. Spine 22:2968–2976
Sandberg D, Lavyne M (1999) Symptomatic spinal epidural lipomatosis after local epidural corticosteroid injections: case report. Neurosurgery 45:162–165
Papadopoulos S (1999) Comments (on Sandberg D et al. "Symptomatic spinal epidural lipomatosis after local epidural corticosteroid injections. Case report"). Neurosurgery 45:165
Qasho R, Ramundo O, Maraglino C, Lunardi P, Ricci G (1997) Epidural lipomatosis with lumbar radiculopathy in one obese patient. Case report and review of literature. Neurosurg Rev 20:206–209
Randall B, Muraki A, Osborn R, Brown F (1986) Epidural lipomatosis with lumbar radiculopathy: CT appearance. J Comput Assist Tomogr 10:1039–1041
Van Rooij W, Bortslap A, Canta L, Tijssen C (1994) Lumbar epidural lipomatosis causing neurogenic claudication in two obese patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 96:181–184
Dihlmann S, Mayer H (1995) Lumbar epidural lipomatosis. Z Rheumatol 54:417–423
Bednar D, Esses S, Kucharczyk W (1990) Symptomatic lumbar epidural lipomatosis in a normal male. A unique case report. Spine 15:52–53
Lipson S, Naheedy M, Kaplan M, Bienfang D (1980) Spinal stenosis caused by epidural lipomatosis in Cushing's syndrome. N Engl J Med 320:36
Pouchot J, Si-Hassen C, Damade R, Bayeux M, Mathieu A, Vinceneux P (1995) Cauda equina compression by epidural lipomatosis in obesity. Effectiveness of weight reduction. J Rheumatol 22:1771–1775
Archer C, Smith K (1982) Extradural lipomatosis simulating an acute herniated nucleus pulposus. J Neurosurg 57:559–562
McCullen G, Spurling G, Webster J (1999) Epidural lipomatosis complicating lumbar steroid injections. J Spinal Disord 12:526–529
Peeters F, Koster P (1991) Epidural lipomatosis simulating spinal canal stenosis or herniated nucleous pulposus. Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 154:342–343
Pennisi A, Meisle W, Dina T (1985) Lymphomatous meningitis and steroid-induced epidural lipomatosis: CT evaluation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9:595–598
Beges C, Rousselin B, Chevrot A, Godefroy D, Vallee C, Berenbaumn F et al. (1994) Epidural lipomatosis. Interest of MRI in weight-reduction treated case. Spine 15:251–254
Benamou PH, Hilliquin P, Chemla N, Chevrot A, Cormier C, Menkes C (1996) Epidural lipomatosis not induced by corticosteroid therapy. Three cases including one in a patient with primary Cushing's disease (review of the literature). Rev Rhum Engl Ed 63:207–212
Berenbaum F, Revel M, Deshays C, Rousselin B, Amor B (1992) Lumbar-radicular pain caused by epidural lipomatosis in an obese patient: recovery after hypocaloric diet. Rev Rhum Mal Ostéoartic 59:225–227
Blanckaert F, Cotten A, Maury F (1995) Epidural lipomatosis. Is it pathogenic? Comments on two case reports. Rachis 7:109–113
Flores A, Sonntag V, Dickman C (1995) Idiopathic spinal epidural lipomatosis: report of two cases and review of the literature. BNIQ 11:22–25
Kurt E, Bakker-Niezen SH (1995) Neurogenic claudication by epidural lipomatosis: a case report and review of the literature. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 97:354–357
Millwater C, Jacovson I, Howard G (1992) Idiopathic epidural lipomatosis as a cause of pain and neurological symptoms attributed initially to radiation damage. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 4:333–334
Romero C, Buzzi A, Lambre H, Martínez A, Meli F, Redondo W, Salas E (1997) Radicular compression caused by lumbosacral epidural lipomatosis. Rev Argent Radiol 61:173–180
Stambough J, Cheeks M, Keiper G (1989) Nonglucocortoid-induced lumbar epidural lipomatosis. A case report and review of literature. J Spinal Disord 2:201–207
Sundram S (1990) CT of epidural lipomatosis: a case report. Radiogr Today 56:26–28
Vázquez L, Ellis A, Saint-Genez D, Patino J, Nogués M (1988) Epidural lipomatosis after renal transplantation: complete recovery without surgery. Transplantation 46:773–774
Zampella E, Duvall E, Sekar B, Langford K, Epstein A, Kirklin J, Morawetz R (1987) Symptomatic spinal epidural lipomatosis as a complication of steroid immunosuppression in cardiac transplant patients. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 67:760–766
Chapman P, Martuza R, Poletti C, Karchmer A (1981) Symptomatic spinal epidural lipomatosis associated with Cushing's syndrome. Neurosurgery 8:724–727
Zentner J, Buchbender K, Vahlensieck M (1995) Spinal epidural lipomatosis as a complication of prolonged corticosteroid therapy. J Neurosurg Sci 39:81–85
Quint D, Boulos R, Sanders W, Mehta B, Patel S, Tiel R (1988) Epidural lipomatosis. Radiology 169:485–490
Lemaire M, Maldague P, Noel P (1998) Corticosteroid-induced epidural lipomatosis. Efficacy of medical treatment. Ann Med Interne (Paris) 149:459–463
Badami J, Hinck V (1982) Symptomatic deposition of epidural fat in a morbidly obese woman. Am J Neuroradiol 3:664–665
Toshniwal P, Glick R (1987) Spinal epidural lipomatosis: report of a case secondary to hypothyroidism and review for the literature. J Neurol 234:172–176
Lisai P Coria C, Crissantu L, Meloni G, Conti M, Achene A (2001) Cauda equina syndrome secondary to idiopathic spinal epidural lipomatosis. Spine 26:307–309
Stern J, Quint D, Sweasey T, Hoff J (1994) Spinal epidural lipomatosis: two new idiopathic cases and a review of the literature. J Spinal Disord 7:343–349
McCormick P (1997) Comments (on Robertson S et al. "Idiopathic spinal epidural lipomatosis"). Neurosurgery 41:74
Cooper P (1997) Comments (on Robertson S et al. "Idiopathic spinal epidural lipomatosis"). Neurosurgery 41:74
Acknowledgement.
The authors are grateful to Eduardo Lassalle, MD, for his continuous academic support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borré, D.G., Borré, G.E., Aude, F. et al. Lumbosacral epidural lipomatosis: MRI grading. Eur Radiol 13, 1709–1721 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-002-1716-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-002-1716-4