Abstract
Objectives
To determine whether neuropathy in diabetic patients with normal nerve conduction studies could be detected by measurements of thermal thresholds and quantification of intraepidermal nerve fibre (IENF) density, and to evaluate differences in parameters between patients with and without neuropathic symptoms.
Methods
A total of 22 patients with and 37 patients without sensory symptoms suggesting distal neuropathy were included. Measurements of warm and cold perception thresholds and skin biopsy for quantification of IENFs were performed distally on the leg. Reference data were used to normalize test results for age and height or gender of individual patients by calculating the Z-scores.
Results
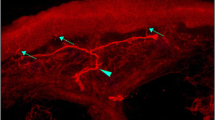
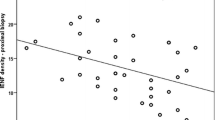
IENF density was significantly reduced in both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients compared to controls (p < 0.001), and in patients with symptoms compared to those without (p = 0.01). Thermal thresholds were significantly elevated (more abnormal) in patients with symptoms compared to controls (p < 0.01), but only for cold perception threshold (CPT) (p < 0.001) in the asymptomatic group. When comparing symptomatic and asymptomatic patients, there was no statistically significant difference in thermal thresholds. Depletion of IENFs in skin biopsy was the most frequent abnormal finding in the subgroup of patients with neuropathic symptoms (36 %) followed by abnormal CPT (27 %).
Conclusion
Patients with diabetes and normal nerve conduction studies had significantly lower IENF density and higher CPT than controls, whether they had symptoms of polyneuropathy or not. In patients with neuropathic symptoms, abnormal IENF density predominated and seemed thus to be the most sensitive tool of detecting small diameter nerve fibre involvement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chao CC, Hsieh SC, Yang WS, LinYH, Lin WM, Tai TY, Hsieh ST (2007) Glycemic control is related to the severity of impaired thermal sensations in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Met Res Rev 23:612–620
Dyck PJ, Hughes RA, O’Brien P (2005) Quantitating overall neuropathic symptoms, impairments and outcomes. In: Dyck PJ, Thomas PK (eds) Peripheral neuropathy. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 1031–1051
Dyck PJ, O’Brien P, Johnson DM, Klein CJ, Dyck JB (2005) Quantitative sensation testing. In: Dyck PJ, Thomas PK (eds) Peripheral neuropathy. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 1063–1093
Gøransson L, Mellgren SI, Lindal S, Omdal R (2004) The effect of age and gender on epidermal nerve fibre density. Neurology 62:774–777
Krämer HH, Rolke R, Bickel A, Birklein F (2004) Thermal thresholds predict painfulness of diabetic neuropathies. Diabetes Care 27:2386–2391
Lin YH, Hsieh SC, Chao CC, Chang YC, Hsieh ST (2005) Influence of aging on thermal and vibratory thresholds of quantitative sensory testing. J Peripher Nerv Syst 10:269–281
Løseth S, Lindal S, Stålberg E, Mellgren SI (2006) Intraepidermal nerve fibre density, quantitative sensory testing and nerve conduction studies in a patient material with symptoms and signs of sensory polyneuropathy. Eur J Neurol 13:105–111
Løseth S, Nebuchennykh M, Stålberg E, Mellgren SI (2007) Medial plantar nerve conduction studies in healthy controls and diabetics. Clin Neurophysiol 118:1155–1161
McArthur JC, Stocks EA, Hauer P, Cornblath DR, Griffin JW (1998) Epidermal nerve fiber density: normative reference range and diagnostic efficiency. Arch Neurol 55:1513–1520
Nebuchennykh M, Løseth S, Mellgren SI (2007) Alternative parameter of quantitative sensory testing: the difference between heat pain and warm perception thresholds in patients with polyneuropathy and healthy individuals. Eur J Neurol 14(Suppl 1):S252
Pittenger GL, Ray M, Burcus NI, McNulty P, Basta B, Vinik AI (2004) Intraepidermal nerve fibers are indicators of small-fiber neuropathy in both diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Diabetes Care 27:1974–1979
Rolke R, Magerl W, Campbell KA, Schalber C, Caspari S, Birklein F, Treede RD (2006) Quantitative sensory testing: a comprehensive protocol for clinical trials. Eur J Pain 10:77–88
Shun CT, Chang YC, Wu HP, Hsieh SC, Lin WM, Lin YH, Tai TY, Hsieh ST (2004) Skin denervation in type 2 diabetes: correlations with diabetic duration and functional impairments. Brain 127:1593–1605
Smith AG, Ramachandran P, Tripp S, Singleton JR (2001) Epidermal nerve innervation in impaired glucose tolerance and diabetes-associated neuropathy. Neurology 57:1701–1704
Sorensen L, Molyneaux L, Yue DK (2006) The level of small nerve fiber dysfunction does not predict pain in diabetic neuropathy: a study using quantitative sensory testing. Clin J Pain 22:261–265
Sorensen L, Molyneaux L, Yue DK (2006) The relationship among pain, sensory loss, and small nerve fibers in diabetes. Diabetes Care 29:883–887
Sumner CJ, Sheth S, Griffin JW, Cornblath DR, Polydefkis M (2003) The spectrum of neuropathy in diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Neurology 60:108–111
Umapathi T, Tan WL, Tan NC, Chan YH (2006) Determinants of epidermal nerve fiber density in normal individuals. Muscle Nerve 33:742–746
Umapathi T, Tan WL, Loke SC, Soon PC, Tavintharan S, Chan YH (2007) Intraepidermal nerve fiber density as a marker of early diabetic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 35:591–598
WHO (1999) Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Report of a WHO Consultation. WHO/NCD/NCS/99.2, Geneve
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Løseth, S., Stålberg, E., Jorde, R. et al. Early diabetic neuropathy: thermal thresholds and intraepidermal nerve fibre density in patients with normal nerve conduction studies. J Neurol 255, 1197–1202 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-0872-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-0872-0