Abstract
Purpose
The dose-dependent effects of sevoflurane and isoflurane anesthesia on glucose tolerance were compared in humans.
Methods
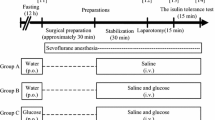
A prospective, randomized clinical study was conducted in 30 patients. The 30 patients were divided randomly into three sevoflurane anesthesia groups (0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 minimum alveolar concentration [MAC]) and three isoflurane anesthesia groups (0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 MAC). Induction of anesthesia was accomplished by inhalation of the volatile agent and nitrous oxide. After induction, anesthesia was maintained at the designated MAC for 15 min without surgical stimulation. The intravenous glucose tolerance test (IVGTT) was performed in these 30 patients while they were under general anesthesia and again several days after surgery in 5 of these patients while they were awake, as a control.
Results
The insulinogenic index (change in concentration of immunoreactive insulin/change in glucose concentration), the acute insulin response, and rates of glucose disappearance were significantly lower in all anesthesia groups than in the control group. However, the insulinogenic index, acute insulin response, and the glucose disappearance rate did not differ significantly among the six anesthesia groups.
Conclusion
Sevoflurane anesthesia impairs glucose tolerance to the same degree as does isoflurane anesthesia. Glucose intolerance during sevoflurane or isoflurane anesthesia is independent of agent and dosage up to 1.5 MAC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F Camu (1973) ArticleTitleCarbohydrate intolerance during halothane anesthesia in dogs Acta Anaesthesiol Belg 24 177–188 Occurrence Handle4773091
F Camu (1976) ArticleTitleImpaired early insulin response to glycemic stimulus during enflurane anesthesia in dogs Acta Anaesthesiol Belg 27 S267–S271
M Diltoer F Camu (1988) ArticleTitleGlucose homeostasis and insulin secretion during isoflurane anesthesia in humans Anesthesiology 68 880–886 Occurrence Handle3288006
S Saho Y Kadota T Sameshima J Miyao T Tsurumaru N Yoshimura (1997) ArticleTitleThe effects of sevoflurane anesthesia on insulin secretion and glucose metabolism in pigs Anesth Analg 84 1359–1365 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000539-199706000-00034 Occurrence Handle9174321
H Iwasaka K Itoh H Miyakawa T Kitano K Taniguchi N Honda (1996) ArticleTitleGlucose intolerance during prolonged sevoflurane anaesthesia Can J Anaesth 43 1059–1061 Occurrence Handle8896859
JP Desborough MG Knowles GM Hall (1998) ArticleTitleEffects of isoflurane-nitrous oxide anesthesia on insulin secretion in female patients Br J Anaesth 80 250–252 Occurrence Handle9602597
MA Pfeifer JB Halter D Porte SuffixJr (1981) ArticleTitleInsulin secretion in diabetes mellitus Am J Med 70 579–588 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0002-9343(81)90579-9 Occurrence Handle7011013
JP Desborough PM Jones SJ Persaud MJ Landon SL Howell (1993) ArticleTitleIsoflurane inhibits insulin secretion from isolated rat pancreatic islets of Langerhans Br J Anaesth 71 873–876 Occurrence Handle8280557
R Gingerich PH Wright RR Paradise (1974) ArticleTitleInhibition by halothane of glucose stimulated insulin secretion in isolated pieces of rat pancreas Anesthesiology 40 449–452 Occurrence Handle4822389
H Staub (1921) ArticleTitleUntersuchungen über den Zuckerstoffwechsel des Menschen (in German) Z Klin Med 91 44–60
K Traugott (1922) ArticleTitleÜber das verhalten des blutzucker-spiegels bei wiederholter und verschiedener art enteraler zuckerzufur und dessen. Bedeutung für die Leberfunktion (in German) Klin Wochenschr 1 892–894 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01715866
DR Derbyshire A Chmielewski D Fell M Vater K Achola G Smith (1983) ArticleTitlePlasma catecholamine responses to tracheal intubation Br J Anaesth 55 855–860 Occurrence Handle6615672
Z Wajima T Inoue T Yoshikawa K Imanaga R Ogawa (2000) ArticleTitleChanges in hemodynamic variables and catecholamine levels after rapid increase in sevoflurane or isoflurane concentration with or without nitrous oxide under endotracheal intubation J Anesth 14 175–179 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s005400070001 Occurrence Handle14564561
D Sbai P Jouvet A Soulier L Penicaud J Merckx JL Bresson (1995) ArticleTitleEffect of halothane anesthesia on glucose utilization and production in adolescents Anesthesiology 82 1154–1159 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000542-199505000-00010 Occurrence Handle7741290
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, T., Nabatame, H. & Tanifuji, Y. Insulin secretion and glucose utilization are impaired under general anesthesia with sevoflurane as well as isoflurane in a concentration-independent manner. J Anesth 19, 277–281 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-005-0341-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-005-0341-1