Abstract
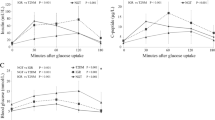
Subjects who develop diabetes have an increased cardiovascular risk even before the appearance of diabetes. The aim of this study was to investigate the glycaemic variability measured by continuous glucose monitoring (CGM CV%) in nondiabetic subjects with metabolic syndrome (MS) and to explore if glycaemic variability was associated with circulating levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), a proinflammatory cytokine, or with an anti-inflammatory factor like adiponectin. Three groups of obese subjects with (MS+: 6m, 8f; BMI 33.1 ± 1.4 mean ± SEM) or without metabolic syndrome (MS−: 2m, 4f; BMI 29.2 ± 2.2) and with MS associated with type 2 diabetes (MS/T2D: 3m, 5f; BMI 32.9 ± 1.4) were investigated. The glycaemic variability was measured in all subjects in terms of CV% of the glycaemic values obtained every 3 min during the course of a 48 h CGM performed using a subcutaneous glucose sensor. The average CGM CV% increased from MS− group (21.1%) to the MS+ group (23.9%) and to the MS+/T2D group (27.4%) but it was not correlated to the CGM mean glycaemia (r = 0.20; P = ns). In some instances, CGM CV% was found higher in MS+ subjects than in some MS+ T2D ones. Stepwise multiple correlation analysis showed that IL-6 predicted CGM CV% (R 2 = 0.35, β = 0.13; P < 0.05) independently from BMI, waist circumference, adiponectin and insulin concentrations. In conclusion, the CGM CV% may contribute to better describe the individual metabolic state and to understand the pathogenesis of endothelial dysfunction in non diabetic subjects with MS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wright E, Scism-Bacon JL, Glass LC (2006) Oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes: the role of fasting and postprandial glycaemia. Int J Clin Pract 60:308–314
Haffner SM, Stern MP, Mazuda HP, Mitchell BD, Patterson JK (1990) Cardiovascular risk factors in confirmed prediabetic individuals. Does the clock for coronary heart disease start ticking before the onset of clinical diabetes? JAMA 263:2893–2898
Hu FB, Stampfer MJ, Haffner SM, Solonen CG, Willett WC, Manson JE (2002) Elevated risk of cardiovascular disease prior to clinical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 25:1129–1134
Stern MP (1995) Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: the “common soil” hypothesis. Diabetes 44:369–374
Ceriello A (2005) Postprandial hyperglycaemia and diabetic complications. Diabetes 54:1–7
Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) (2001) Executive summary of the third report of the national cholesterol education program (NCEP). JAMA 285:2486–2497
The expert committee on the Diagnosis, Classification of Diabetes Mellitus (2003) Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 26(suppl 1):s5–s20
Matthews D-R, Hosker J-P, Rudenski A-S, Naylor B-A, Treacher D-F, Turner R-C (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Maran A, Poscia A (2002) Continuous subcutaneous glucose monitoring; the GlucoDay system. Diab Nutr Metab 15:429–433
Wentholt IH, Vallebregt MA, Hart AA, Hoekstra JB, Devries JH (2005) Comparison of a needle-type and a microdialysis continuous glucose monitor in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 28:2871–2876
De Block C, Van Gaal L, Keenoy BM, Rogiers P (2006) Intensive insulin therapy in the intensive care unit. Diabetes Care 29:1750–1756
Koh KK, Han SH, Quon MJ (2005) Inflammatory markers and the metabolic syndrome. JACC 46:1978–1985
Borst SE (2004) The role of TNF-α in insulin resistance. Endocrine 23:177–182
Waite KJ, Floyd ZE, Arbour-Reily P, Stephens JM (2001) Interferon-γ-induced regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and STATs in adipocytes. J Biol Chem 276:7062–7068
Wellen KE, Hotamisligil GS (2003) Obesity-induced inflammatory changes in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 112:1785–1788
Weier C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K, Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE, Tataranni PA (2001) Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:1930–1935
Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Okamoto Y, Iwahashi H, Kuriyama H, Ouchi N, Maeda K, Nishida M, Kihara S, Sakai N, Nakajima T, Hasegawa K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Hanafusa T, Matsuzawa Y (2000) Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:1595–1599
Spranger J, Kroke A, Mohlig M, Bergmann MM, Ristow M, Boeing H, Pfeiffer AF (2003) Adiponectin and protection against type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lancet 361:226–228
Snijder MB, Heine RJ, Seidell JC, Bouter LM, Stehouwer CDA, Nijpels G, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Shimomura I, Dekker JM (2006) Associations of adiponectin levels with incident impaired glucose metabolism and type 2 diabetes in older men and women. Diabetes Care 29:2498–2503
Motoshima H, Wu X, Sinha MK, Hardy VE, Rosato EL, Barbot DJ, Rosato FE, Goldstein BJ (2002) Differential regulation of adiponectin secretion from cultured human omental and subcutaneous adipocytes: effects of insulin and rosiglitazone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:5662–5667
Kumada M, Kihara S, Sumitsuji S, Kawamoto T, Matsumoto S, Ouchi N, Arita Y, Okamoto Y, Shimomura I, Hiraoka H, Nakamura T, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Osaka CAD Study Group (2003) Association of hypoadiponectinemia with coronary artery disease in men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:85–89
Pischon T, Girman CJ, Hotamisligil GS, Rifai N, Hu FB, Rimm EB (2004) Plasma adiponectin levels and risk of myocardial infarction in men. JAMA 291:1730–1737
Kojima S, Funahashi T, Maruyoshi H, Honda O, Suguyama S, Kawano H, Soejima H, Miyamoto S, Hokamaki J, Sakamoto T, Yoshimura M, Kitagawa A, Matsuzawa Y, Ogawa H (2005) Levels of the adipocyte-derived plasma protein, adiponectin, have a close relationship with atheroma. Thromb Res 115:483–490
Pilz S, Horejsi R, Moller R, Almer G, Scharnagl H, Stojakovic T, Dimitrova R, Weihrauch G, Borkenstein M, Maerz W, Schauenstein K, Mangge H (2005) Early atherosclerosis in obese juveniles is associated with low serum levels of adiponectin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:4792–4796
Lo J, Dolan SE, Kanter JR, Hemphill LC, Connelly JM, Lees RS, Grinspoon SK (2006) Effects of obesity, body composition, and adiponectin on carotid intima-media thickness in healthy women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:1677–1682
Yokoyama H, Emoto M, Mori K, Araki T, Teramura M, Koyama H, Shoji T, Inaba M, Nishizawa Y (2006) Plasma adiponectin level is associated with insulin-stimulated nonoxidative glucose disposal. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:290–294
You T, Yang R, Lyles MF, Gong D, Nicklas BJ (2005) Abdominal adipose tissue cytokine gene expression: relationship to obesity and metabolic risk factors. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288:741–747
Rotter V, Nagaev I, Smith U (2003) Interleukin-6 (IL-6) induces insulin resistance in 3T3–L1 adipocytes and is, like IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor-α, overexpressed in human fat cells from insulin-resistant subjects. J Biol Chem 278:45777–45784
Ouchi N, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Nakamura T, Nishida M, Kumada M, Okamoto Y, Ohashi K, Nagaretani H, Kishida K, Nishizawa H, Maeda N, Kobayashi H, Hiraoka H, Matsuzawa Y (2003) Reciprocal association of C-reactive protein with adiponectin in blood stream and adipose tissue. Circulation 107:671–674
Fasshauer M, Klein J, Neumann S, Eszlinger M, Paschke R (2002) Hormonal regulation of adiponectin gene expression in 3T3–L1 adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:1084–1089
Singleton JR, Smith AG, Russell JW, Feldman EL (2003) Microvascular complications of impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes 52:2867–2873
Hirsh IB, Brownlee M (2005) Should minimal blood glucose variability become the gold standard of glycaemic control? J Diabetes Complications 19:178–181
Hirsh IB (2005) Intensifying insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Med 118s5A:21s–26s
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by the Italian Ministero dell’Università e della Ricerca Scientifica e Tecnologica (MURST funds 60% project 2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buscemi, S., Verga, S., Cottone, S. et al. Glycaemic variability and inflammation in subjects with metabolic syndrome. Acta Diabetol 46, 55–61 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-008-0061-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-008-0061-8