Summary
Objective. To compare the respective effects of established measures used for management of traumatic brain injury (TBI) patients on cerebral blood flow (CBF) and cerebral metabolic rates of oxygen (CMRO2), glucose (CMRGlc) and lactate (CMRLct).
Methods. Thirty-six patients suffering from severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) were prospectively evaluated. In all patients baseline assessments were compared with that following moderate hyperventilation (reducing PaCO2 from 36 ± 4 to 32 ± 4 mmHg) and with that produced by administration of 0.5 gr/kg mannitol 20% intravenously. Intracranial and cerebral perfusion pressure (ICP, CPP), CBF and arterial jugular differences in oxygen, glucose and lactate contents were measured for calculation of CMRO2, CMRGlc and CMRLct.
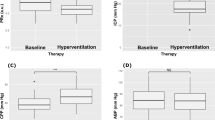
Results. Following hyperventilation, CBF was significantly reduced (P < 0.0001). CBF remained most often above the ischemic range although values less than 30 ml·100 gr−1·min−1 were found in 27.8% of patients. CBF reduction was associated with concurrent decrease in CMRO2, anaerobic hyperglycolysis and subsequent lactate production. In contrast, mannitol resulted in significant albeit moderate improvement of cerebral perfusion. However, administration of mannitol had no ostensible effect either on oxidative or glucose metabolism and lactate balance remained mostly unaffected.
Conclusions. Moderate hyperventilation may exacerbate pre-existing impairment of cerebral blood flow and metabolism in TBI patients and should be therefore carefully used under appropriate monitoring. Our findings rather support the use of mannitol for ICP control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AM Alberico JD Ward SC Choi A Marmarou HF Young (1987) ArticleTitleOutcome after severe head injury. Relationship to mass lesions, diffuse injury, and ICP course in pediatric and adult patients J Neurosurg 67 648–656 Occurrence Handle3668633 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c%2FjsFWrtQ%3D%3D
M Bergsneider DA Hovda E Shalmon DF Kelly PM Vespa NA Martin ME Phelps DL McArthur MJ Caron JF Kraus DP Becker (1997) ArticleTitleCerebral hyperglycolysis following severe traumatic brain injury in humans: a positron emission tomography study J Neurosurg 86 241–251 Occurrence Handle9010426 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s7mtlKiuw%3D%3D
GJ Bouma JP Muizelaar SC Choi PG Newlon HF Young (1991) ArticleTitleCerebral circulation and metabolism after severe traumatic brain injury: the elusive role of ischemia J Neurosurg 75 685–693 Occurrence Handle1919689 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK38%2FhsVagtA%3D%3D
T Clausen A Scharf M Menzel J Soukup C Holz A Rieger F Hanisch E Brath N Nemeth I Miko P Vajkoczy J Radke D Henze (2004) ArticleTitleInfluence of moderate and profound hyperventilation on cerebral blood flow, oxygenation and metabolism Brain Res 1019 113–123 Occurrence Handle15306245 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXmslemsLw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.brainres.2004.05.099
JP Coles PS Minhas TD Fryer P Smielewski F Aigbirihio T Donovan SP Downey G Williams D Chatfield JC Matthews AK Gupta TA Carpenter JC Clark JD Pickard DK Menon (2002) ArticleTitleEffect of hyperventilation on cerebral blood flow in traumatic head injury: clinical relevance and monitoring correlates Crit Care Med 30 1950–1959 Occurrence Handle12352026 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnsVWmsbo%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00003246-200209000-00002
J Cruz G Minoja K Okuchi (2001) ArticleTitleImproving clinical outcomes from acute subdural hematomas with the emergency preoperative administration of high doses of mannitol: a randomized trial Neurosurgery 49 864–871 Occurrence Handle11564247 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MrjslKrsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200110000-00016
J Cruz G Minoja K Okuchi (2002) ArticleTitleMajor clinical and physiological benefits of early high doses of mannitol for intraparenchymal temporal lobe hemorrhages with abnormal pupillary widening: a randomized trial Neurosurgery 51 628–637 Occurrence Handle12188940 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-200209000-00006
J Cruz G Minoja K Okuchi E Facco (2004) ArticleTitleSuccessful use of the new high-dose mannitol treatment in patients with Glasgow Coma Scale scores of 3 and bilateral abnormal pupillary widening: a randomized trial J Neurosurg 100 376–383 Occurrence Handle15035271 Occurrence Handle10.3171/jns.2004.100.3.0376
MN Diringer TO Videen K Yundt AR Zazulia V Aiyagari RG Dacey SuffixJr RL Grubb WJ Powers (2002) ArticleTitleRegional cerebrovascular and metabolic effects of hyperventilation after severe traumatic brain injury J Neurosurg 96 103–108 Occurrence Handle11794590
MN Diringer K Yundt TO Videen RE Adams AR Zazulia E Deibert V Aiyagari RG Dacey SuffixJr RL Grubb SuffixJr WJ Powers (2000) ArticleTitleNo reduction in cerebral metabolism as a result of early moderate hyperventilation following severe traumatic brain injury J Neurosurg 92 7–13 Occurrence Handle10616076 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2FotFyhsA%3D%3D
MD Ginsberg W Zhao OF Alonso JY Loor-Estades WD Dietrich R Busto (1997) ArticleTitleUncoupling of local cerebral glucose metabolism and blood flow after acute fluid-percussion injury in rats Am J Physiol 272 H2859–H2868 Occurrence Handle9227566 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXksVSrs78%3D
TC Glenn DF Kelly WJ Boscardin DL McArthur P Vespa M Oertel DA Hovda M Bergsneider L Hillered NA Martin (2003) ArticleTitleEnergy dysfunction as a predictor of outcome after moderate or severe head injury: indices of oxygen, glucose, and lactate metabolism J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23 1239–1250 Occurrence Handle14526234 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnslaqsbc%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/01.WCB.0000089833.23606.7F
JL Jaggi WD Obrist TA Gennarelli TW Langfitt (1990) ArticleTitleRelationship of early cerebral blood flow and metabolism to outcome in acute head injury J Neurosurg 72 176–182 Occurrence Handle2295915 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3c7htFyhtA%3D%3D
B Jennett M Bond (1975) ArticleTitleAssessment of outcome after severe brain damage Lancet 1 480–484 Occurrence Handle46957 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE2M7hsl2jsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0140-6736(75)92830-5
PJ Kirkpatrick P Smielewski S Piechnik JD Pickard M Czosnyka (1996) ArticleTitleEarly effects of mannitol in patients with head injuries assessed using bedside multimodality monitoring Neurosurgery 39 714–720 Occurrence Handle8880763 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s%2FjsFWjtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00006123-199610000-00013
N Lundberg A Kjallquist C Bien (1959) ArticleTitleReduction of increased intracranial pressure by hyperventilation. A therapeutic aid in neurological surgery Acta Psychiatr Scand 34 IssueID[Suppl] 139 1–64 Occurrence Handle14418913 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaF3c7ntFGqtg%3D%3D
DW Marion A Puccio SR Wisniewski P Kochanek CE Dixon L Bullian P Carlier (2002) ArticleTitleEffect of hyperventilation on extracellular concentrations of glutamate, lactate, pyruvate, and local cerebral blood flow in patients with severe traumatic brain injury Crit Care Med 30 2619–2625 Occurrence Handle12483048 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XpsFSgsb4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00003246-200212000-00001
NA Martin RV Patwardhan MJ Alexander CZ Africk JH Lee E Shalmon DA Hovda DP Becker (1997) ArticleTitleCharacterization of cerebral hemodynamic phases following severe head trauma: hypoperfusion, hyperemia, and vasospasm J Neurosurg 87 9–19 Occurrence Handle9202259 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2szksFOltQ%3D%3D
JD Miller DP Becker JD Ward HG Sullivan WE Adams MJ Rosner (1977) ArticleTitleSignificance of intracranial hypertension in severe head injury J Neurosurg 47 503–516 Occurrence Handle903804 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE1c%2Fgslaktw%3D%3D
JP Muizelaar A Marmarou JD Ward HA Kontos SC Choi DP Becker H Gruemer HF Young (1991) ArticleTitleAdverse effects of prolonged hyperventilation in patients with severe head injury: a randomized clinical trial J Neurosurg 75 731–739 Occurrence Handle1919695 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK38%2FhsVansA%3D%3D
WD Obrist TW Langfitt JL Jaggi J Cruz TA Gennarelli (1984) ArticleTitleCerebral blood flow and metabolism in comatose patients with acute head injury. Relationship to intracranial hypertension J Neurosurg 61 241–253 Occurrence Handle6737048 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2c3ktF2lug%3D%3D
M Oertel DF Kelly JH Lee DL McArthur TC Glenn P Vespa WJ Boscardin DA Hovda NA Martin (2002) ArticleTitleEfficacy of hyperventilation, blood pressure elevation, and metabolic suppression therapy in controlling intracranial pressure after head injury J Neurosurg 97 1045–1053 Occurrence Handle12450025
RD Rothoerl KM Schebesch C Woertgen A Brawanski (2003) ArticleTitleInternal carotid artery volume flow correlates to rCBF measurements Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145 943–947 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3srkvVektg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00701-003-0108-0
RD Rothoerl KM Schebesch C Woertgen A Brawanski (2005) ArticleTitleUltrasonic blood flow volume assessment in the extracranial internal carotid artery in arteriovenous malformations Neurol Res 27 209–211 Occurrence Handle15829185 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD2M7ps1ensg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1179/016164105X35567
TG Saul TB Ducker (1982) ArticleTitleEffect of intracranial pressure monitoring and aggressive treatment on mortality in severe head injury J Neurosurg 56 498–503 Occurrence Handle6801218 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL387ksVOrsw%3D%3D
JF Soustiel TC Glenn V Shik J Boscardin E Mahamid M Zaaroor (2005) ArticleTitleMonitoring of cerebral blood flow and metabolism in traumatic brain injury J Neurotrauma 22 955–965 Occurrence Handle16156711 Occurrence Handle10.1089/neu.2005.22.955
JF Soustiel TC Glenn P Vespa B Rinsky C Hanuscin NA Martin (2003) ArticleTitleAssessment of cerebral blood flow by means of blood-flow-volume measurement in the internal carotid artery: comparative study with a 133xenon clearance technique Stroke 34 1876–1880 Occurrence Handle12843349 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3szmtFeksA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1161/01.STR.0000080942.32331.39
JF Soustiel E Levy M Zaaroor R Bibi S Lukaschuk D Manor (2002) ArticleTitleA new angle-independent Doppler ultrasonic device for assessment of blood flow volume in the extracranial internal carotid artery J Ultrasound Med 21 1405–1412 Occurrence Handle12494983
G Teasdale B Jennett (1974) ArticleTitleAssessment of coma and impaired consciousness. A practical scale Lancet 2 81–84 Occurrence Handle4136544 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE2c3pvVGjuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0140-6736(74)91639-0
S Thomas ML Prins M Samii DA Hovda (2000) ArticleTitleCerebral metabolic response to traumatic brain injury sustained early in development: a 2-deoxy-D-glucose autoradiographic study J Neurotrauma 17 649–665 Occurrence Handle10972242 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2Fmslyqug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1089/089771500415409
BH Verweij JP Muizelaar FC Vinas PL Peterson Y Xiong CP Lee (2000) ArticleTitleImpaired cerebral mitochondrial function after traumatic brain injury in humans J Neurosurg 93 815–820 Occurrence Handle11059663 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3crgslygsw%3D%3D
Y Xiong Q Gu PL Peterson JP Muizelaar CP Lee (1997) ArticleTitleMitochondrial dysfunction and calcium perturbation induced by traumatic brain injury J Neurotrauma 14 23–34 Occurrence Handle9048308 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s3gtVeksQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1089/neu.1997.14.23
T Yamaki Y Imahori Y Ohmori E Yoshino T Hohri T Ebisu S Ueda (1996) ArticleTitleCerebral hemodynamics and metabolism of severe diffuse brain injury measured by PET J Nucl Med 37 1166–1170 Occurrence Handle8965189 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK283mvVWntw%3D%3D
MS Yang DS DeWitt DP Becker RL Hayes (1985) ArticleTitleRegional brain metabolite levels following mild experimental head injury in the cat J Neurosurg 63 617–621 Occurrence Handle4032026 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXlslKmtrg%3D Occurrence Handle10.3171/jns.1985.63.4.0617
M Zweinenberg-Lee JP Muizelaar (2004) Clinical pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury HR Winn (Eds) Youmans neurological surgery Saunders Philadelphia 5039–5064
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soustiel, J., Mahamid, E., Chistyakov, A. et al. Comparison of moderate hyperventilation and mannitol for control of intracranial pressure control in patients with severe traumatic brain injury – a study of cerebral blood flow and metabolism. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148, 845–851 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-006-0792-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-006-0792-7