Abstract
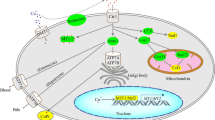
Protein deglycation, a new form of protein repair, involves several enzymes. Fructosamine-3-kinase (FN3K), an enzyme found in mammals and birds, phosphorylates fructosamines on the third carbon of their sugar moiety, making them unstable and causing them to detach from proteins. This enzyme acts particularly well on fructose-epsilon-lysine, both in free form and in the accessible regions of proteins. Mice deficient in FN3K accumulate protein-bound fructosamines and free fructoselysine, indicating that the deglycation mechanism initiated by FN3K is operative in vivo. Mammals and birds also have an enzyme designated ‘FN3K-related protein’ (FN3KRP), which shares ≈65% sequence identity with FN3K. Unlike FN3K, FN3KRP does not phosphorylate fructosamines, but acts on ribulosamines and erythrulosamines. As with FN3K, the third carbon is phosphorylated and this leads to destabilization of the ketoamines. Experiments with intact erythrocytes indicate that FN3KRP is also a protein-repair enzyme. Its physiological substrates are most likely formed from ribose 5-phosphate and erythrose 4-phosphate, which give rise to ketoamine 5- or 4-phosphates. The latter are dephosphorylated by ‘low-molecular-weight protein-tyrosine-phosphatase-A’ (LMW-PTP-A) before FN3KRP transfers a phosphate on the third carbon. The specificity of FN3K homologues present in plants and bacteria is similar to that of mammalian FN3KRP, suggesting that deglycation of ribulosamines and/or erythrulosamines is an ancient mechanism. Mammalian cells contain also a phosphatase acting on fructosamine 6-phosphates, which result from the reaction of proteins with glucose 6-phosphate.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baynes JW, Watkins NG, Fisher CI, Hull CJ, Patrick JS, Ahmed MU, Dunn JA, Thorpe SR (1989) The Amadori product on protein: structure and reactions. Prog Clin Biol Res 304:43–67
Clarke S (2003) Aging as war between chemical, biochemical processes: protein methylation, the recognition of age-damaged proteins for repair. Ageing Res Rev 2:263–285
Collard F, Delpierre G, Stroobant V, Matthijs G, Van Schaftingen E (2003) A mammalian protein homologous to fructosamine-3-kinase is a ketosamine-3-kinase acting on psicosamines and ribulosamines but not on fructosamines. Diabetes 52:2888–2895
Collard F, Wiame E, Bergans N, Fortpied J, Vertommen D, Vanstapel F, Delpierre G, Van Schaftingen E (2004) Fructosamine 3-kinase-related protein and deglycation in human erythrocytes. Biochem J 382:137–143
Collard F, Zhang J, Nemet I, Qanungo KR, Monnier VM, Yee VC (2008) Crystal structure of the deglycating enzyme fructosamine oxidase (amadoriase II). J Biol Chem 283:27007–27016
Conner JR, Beisswenger PJ, Szwergold BS (2004) The expression of the genes for fructosamine-3-kinase and fructosamine-3-kinase-related protein appears to be constitutive and unaffected by environmental signals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 323:932–936
Delpierre G, Rider MH, Collard F, Stroobant V, Vanstapel F, Santos H, Van Schaftingen E (2000) Identification, cloning, and heterologous expression of a mammalian fructosamine-3-kinase. Diabetes 49:1627–1634
Delpierre G, Collard F, Fortpied J, Van Schaftingen E (2002) Fructosamine 3-kinase is involved in an intracellular deglycation pathway in human erythrocytes. Biochem J 365:801–808
Delpierre G, Vertommen D, Communi D, Rider MH, Van Schaftingen E (2004) Identification of fructosamine residues deglycated by fructosamine-3-kinase in human hemoglobin. J Biol Chem 279:27613–27620
Delplanque J, Delpierre G, Opperdoes FR, Van Schaftingen E (2004) Tissue distribution and evolution of fructosamine 3-kinase and fructosamine 3-kinase-related protein. J Biol Chem 279:46606–46613
Drozak J, Veiga-da-Cunha M, Vertommen D, Stroobant V, Van Schaftingen E (2010) Molecular identification of carnosine synthase as ATP-grasp domain-containing protein 1 (ATPGD1). J Biol Chem 285:9346–9356
Fortpied J, Gemayel R, Stroobant V, van Schaftingen E (2005) Plant ribulosamine/erythrulosamine 3-kinase, a putative protein-repair enzyme. Biochem J 388:795–802
Fortpied J, Maliekal P, Vertommen D, Van Schaftingen E (2006) Magnesium-dependent phosphatase-1 is a protein-fructosamine-6-phosphatase potentially involved in glycation repair. J Biol Chem 281:18378–18385
Fortpied J, Gemayel R, Vertommen D, Van Schaftingen E (2007) Identification of protein-ribulosamine-5-phosphatase as human low-molecular-mass protein tyrosine phosphatase-A. Biochem J 406:139–145
Galperin MY, Moroz OV, Wilson KS, Murzin AG (2006) House cleaning, a part of good housekeeping. Mol Microbiol 59:5–19
Gemayel R, Fortpied J, Rzem R, Vertommen D, Veiga-da-Cunha M, Van Schaftingen E (2007) Many fructosamine 3-kinase homologues in bacteria are ribulosamine/erythrulosamine 3-kinases potentially involved in protein deglycation. FEBS J 274:4360–4374
Hodge JE (1955) The Amadori rearrangement. Adv Carbohydr Chem 10:169–205
Kim E, Lowenson JD, MacLaren DC, Clarke S, Young SG (1997) Deficiency of a protein-repair enzyme results in the accumulation of altered proteins, retardation of growth, and fatal seizures in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6132–6137
Krause R, Oehme A, Wolf K, Henle T (2006) A convenient HPLC assay for the determination of fructosamine-3-kinase activity in erythrocytes. Anal Bioanal Chem 386:2019–2025
Leslie RD, Cohen RM (2009) Biologic variability in plasma glucose, hemoglobin A1c and advanced glycation end products associated with diabetes complications. J Diabetes Sci Technol 3:635–643
Mohás M, Kisfali P, Baricza E, Mérei A, Maász A, Cseh J, Mikolás E, Szijártó IA, Melegh B, Wittmann I (2010) A polymorphism within the fructosamine-3-kinase gene is associated with HbA1c Levels and the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 118:209–212
Monnier VM, Wu X (2003) Enzymatic deglycation with amadoriase enzymes from Aspergillus sp. as a potential strategy against the complications of diabetes and aging. Biochem Soc Trans 31:1349–1353
Moskovitz J (2005) Methionine sulfoxide reductases: ubiquitous enzymes involved in antioxidant defense, protein regulation, and prevention of aging-associated diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1703:213–219
Pascal SM, Veiga-da-Cunha M, Gilon P, Van Schaftingen E, Jonas JC (2010) Effects of fructosamine-3-kinase deficiency on function and survival of mouse pancreatic islets after prolonged culture in high glucose or ribose concentrations. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 298:E586–E596
Payne LS, Brown PM, Middleditch M, Baker E, Cooper GJ, Loomes KM (2008) Mapping of the ATP-binding domain of human fructosamine 3-kinase-related protein by affinity labelling with 5′-[p-(fluorosulfonyl)benzoyl]adenosine. Biochem J 416:281–288
Peisach E, Selengut JD, Dunaway-Mariano D, Allen KN (2004) X-ray crystal structure of the hypothetical phosphotyrosine phosphatase MDP-1 of the haloacid dehalogenase superfamily. Biochemistry 43:12770–12779
Petersen A, Szwergold BS, Kappler F, Weingarten M, Brown TR (1990) Identification of sorbitol 3-phosphate and fructose 3-phosphate in normal and diabetic human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem 265:17424–17427
Petersen A, Kappler F, Szwergold BS, Brown TR (1992) Fructose metabolism in the human erythrocyte. Phosphorylation to fructose 3-phosphate. Biochem J 284:363–366
Phillips SA, Thornalley PJ (1993) The formation of methylglyoxal from triose phosphates. Investigation using a specific assay for methylglyoxal. Eur J Biochem 212:101–105
Richard JP (1993) Mechanism for the formation of methylglyoxal from triosephosphates. Biochem Soc Trans 21:549–553
Selengut JD (2001) MDP-1 is a new and distinct member of the haloacid dehalogenase family of aspartate-dependent phosphohydrolases. Biochemistry 40:12704–12711
Selengut JD, Levine RL (2000) MDP-1: a novel eukaryotic magnesium-dependent phosphatase. Biochemistry 39:8315–8324
Szwergold BS (2005) Carnosine and anserine act as effective transglycating agents in decomposition of aldose-derived Schiff bases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 336:36–41
Szwergold BS (2006) Alpha-thiolamines such as cysteine and cysteamine act as effective transglycating agents due to formation of irreversible thiazolidine derivatives. Med Hypotheses 66:698–707
Szwergold BS, Kappler F, Brown TR (1990) Identification of fructose 3-phosphate in the lens of diabetic rats. Science 247:451–454
Szwergold BS, Howell S, Beisswenger PJ (2001) Human fructosamine-3-kinase: purification, sequencing, substrate specificity, and evidence of activity in vivo. Diabetes 50:2139–2147
Szwergold B, Manevich Y, Payne L, Loomes K (2007) Fructosamine-3-kinase-related-protein phosphorylates glucitolamines on the C-4 hydroxyl: novel substrate specificity of an enigmatic enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 361:870–875
Van Schaftingen E, Rzem R, Veiga-da-Cunha M (2009) l-2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria, a disorder of metabolite repair. J Inherit Metab Dis 32:135–142
Veiga-da-Cunha M, Jacquemin P, Delpierre G, Godfraind C, Theate I, Vertommen D, Clotman F, Lemaigre F, Devuyst O, Van Schaftingen E (2006) Increased protein glycation in fructosamine-3-kinase deficient mice. Biochem J 399:257–264
Wiame E, Delpierre G, Collard F, Van Schaftingen E (2002) Identification of a pathway for the utilization of the Amadori product fructoselysine in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 277:42523–42529
Wiame E, Duquenne A, Delpierre G, Van Schaftingen E (2004) Identification of enzymes acting on alpha-glycated amino acids in Bacillus subtilis. FEBS Lett 577:469–472
Wiame E, Lamosa P, Santos H, Van Schaftingen E (2005) Identification of glucoselysine-6-phosphate deglycase, an enzyme involved in the metabolism of the fructation product glucoselysine. Biochem J 392:263–269
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Interuniversity Attraction Poles Program-Belgian Science Policy, by the Belgian Scientific Fund for Medical Research (FRSM), and by the DIANE centre of excellence programme of the Région Wallonne. FC and EW are Chargés de Recherche and MVDC is Chercheur Qualifié of the Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Schaftingen, E., Collard, F., Wiame, E. et al. Enzymatic repair of Amadori products. Amino Acids 42, 1143–1150 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0780-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0780-3