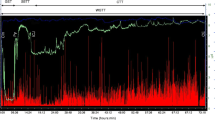
Abstract
We compared quantitative sudomotor axon-reflex test responses in persons with normal and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT). Responses were significantly impaired in those with IGT, which may be indicative of early distal small fiber neuropathy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Whitt MC, Irwin ML, Swartz AM, Strath SJ, O’Brien WL, Bassett DR Jr, Schmitz KH, Emplaincourt PO, Jacobs DR Jr, Leon AS (2000) Compendium of physical activities: an update of activity codes and MET intensities. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:S498–S504
Braune HJ, Horter C (1996) Sympathetic skin response in diabetic neuropathy: a prospective clinical and neurophysiological trial on 100 patients. J Neurol Sci 138:120–124
Cappellari A, Airaghi L, Capra R, Ciammola A, Branchi A, Levi Minzi G, Bresolin N (2005) Early peripheral nerve abnormalities in impaired glucose tolerance. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 45:241–244
Franklin GM, Kahn LB, Baxter J, Marshall JA, Hamman RF (1990) Sensory neuropathy in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The San Luis Valley Diabetes Study. Am J Epidemiol 131:633–643
Fujimoto WY, Leonetti DL, Kinyoun JL, Shuman WP, Stolov WC, Wahl PW (1987) Prevalence of complications among second-generation Japanese-American men with diabetes, impaired glucose tolerance, or normal glucose tolerance. Diabetes 36:730–739
Hoeldtke RD, Bryner KD, Horvath GG, Phares RW, Broy LF, Hobbs GR (2001) Redistribution of sudomotor responses is an early sign of sympathetic dysfunction in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 50:436–443
Kaholokula JK, Haynes SN, Grandinetti A, Chang HK (2003) Biological, psychosocial, and sociodemographic variables associated with depressive symptoms in persons with type 2 diabetes. J Behav Med 26:435–458
Kriska AM, Knowler WC, LaPorte RE, Drash AL, Wing RR, Blair SN, Bennett PH, Kuller LH (1990) Development of a questionnaire to examine the relationship of physical activity and diabetes in the Pima Indians. Diabetes Care 13:401–411
Low PA (2004) Evaluation of sudomotor function. Clin Neurophysiol 115:1506–1513
Low PA, Denq JC, Opfer-Gehrking TL, Dyck PJ, O’Brien PC, Slezak JM (1997) Effect of age and gender on sudomotor and cardiovagal function and blood pressure response to tilt in normal subjects. Muscle Nerve 20:1561–1568
Low PA, Zimmerman BR, Dyck PJ (1986) Comparison of distal sympathetic with vagal function in diabetic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 9:592–596
Novella SP, Inzucchi SE, Goldstein JM (2001) The frequency of undiagnosed diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in patients with idiopathic sensory neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 24:1229–1231
Puavilai G, Chanprasertyotin S, Sriphrapradaeng A (1999) Diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus and other categories of glucose intolerance: 1997 criteria by the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus (ADA), 1998 WHO consultation criteria, and 1985 WHO criteria. World Health Organization. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 44:21–26
Singleton JR, Smith AG, Bromberg MB (2001) Increased prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance in patients with painful sensory neuropathy. Diabetes Care 24:1448–1453
Sumner CJ, Sheth S, Griffin JW, Cornblath DR, Polydefkis M (2003) The spectrum of neuropathy in diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Neurology 60:108–111
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (grant # 1-S11 NS043364-02 and U54NS039406-05S1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grandinetti, A., Chow, D.C., Sletten, D.M. et al. Impaired glucose tolerance is associated with postganglionic sudomotor impairment. Clin Auton Res 17, 231–233 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-007-0426-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-007-0426-z