Abstract
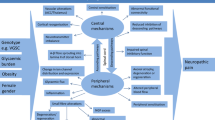
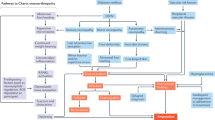
Painful diabetic polyneuropathy (PDPN) is generally considered a variant of diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN) but the identification of distinctive aspects that characterize painful compared with painless DPN has however been addressed in many studies, mainly with the purpose of better understanding the mechanisms of neuropathic pain in the scenario of peripheral nerve damage of DPN, of determining risk markers for pain development, and also of recognizing who might respond to treatments. This review is aimed at examining available literature dealing with the issue of similarities and differences between painful and painless DPN in an attempt to respond to the question of whether painful and painless DPN are the same disease or not and to address the conundrum of why some people develop the insensate variety of DPN whilst others experience distressing pain. Thus, from the perspective of comparing painful with painless forms of DPN, this review considers the clinical correlates of PDPN, its distinctive framework of symptoms, signs, and nerve functional and structural abnormalities, the question of large and small fiber involvement, the peripheral pain mechanisms, the central processing of pain and some new insights into the pathogenesis of pain in peripheral polyneuropathies and PDPN.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
• Tesfaye S, Boulton AJ, Dyck PJ, Freeman R, Horowitz M, Kempler P, et al. Diabetic neuropathies: update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:2285–93. This paper is the summary report of the Toronto consensus meeting on diabetic neuropathy. It provides novel insights into the definition and diagnosis of different forms of diabetic neuropathy.
Treede RD, Jensen TS, Campbell JN, Cruccu G, Dostrovsky JO, Griffin JW, et al. Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology. 2008;70:1630–5.
Daousi C, MacFarlane IA, Woodward A, Nurmikko TJ, Bundred PE, Benbow SJ. Chronic painful peripheral neuropathy in an urban community: a controlled comparison of people with and without diabetes. Diabet Med. 2004;21:976–82.
Davies M, Brophy S, Williams R, Taylor A. The prevalence, severity, and impact of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:1518–22.
Ziegler D, Rathmann W, Dickhaus T, Meisinger C, Mielck A, KORA Study Group. Neuropathic pain in diabetes, prediabetes and normal glucose tolerance: the MONICA/KORA Augsburg Surveys S2 and S3. Pain Med. 2009;10:393–400.
Van Acker K, Bouhassira D, De Bacquer D, Weiss S, Matthys K, Raemen H, et al. Prevalence and impact on quality of life of peripheral neuropathy with or without neuropathic pain in type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients attending hospital outpatients clinics. Diabetes Metab. 2009;35:206–13.
Abbott CA, Malik RA, van Ross ER, Kulkarni J, Boulton AJ. Prevalence and characteristics of painful diabetic neuropathy in a large community-based diabetic population in the U.K. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:2220–4.
Miralles-García JM, de Pablos-Velasco P, Cabrerizo L, Pérez M, López-Gómez V, Sociedad Española de Endocrinología y Nutrición. Prevalence of distal diabetic polyneuropathy using quantitative sensory methods in a population with diabetes of more than 10 years’ disease duration. Endocrinol Nutr. 2010;57:414–20.
Fedele D, Comi G, Coscelli C, Cucinotta D, Feldman EL, Ghirlanda G, et al. A multicenter study on the prevalence of diabetic neuropathy in Italy. Italian Diabetic neuropathy Committee. Diabetes Care. 1997;20:836–43.
Shaw JE, Zimmet PZ, Gries FA, Ziegler D. Epidemiology of diabetic neuropathy. In: Gries FA, Cameron NE, Low PA, Ziegler D, editors. Textbook of diabetic neuropathy. Stuttgard: Thieme; 2003. p. 64–82.
Gore M, Brandenburg NA, Dukes E, Hoffman DL, Tai KS, Stacey B, et al. Pain severity in diabetic peripheral neuropathy is associated with patient functioning, symptom levels of anxiety and depression, and sleep. J Pain Symptom Manag. 2005;30:374–85.
Tölle T, Xu X, Sadosky AB. Painful diabetic neuropathy: a cross-sectional survey of health state impairment and treatment patterns. J Diabetes Complications. 2006;20:26–33.
Fishbain DA, Hall JA, Risser RC, Gonzales JS. Does pain cause the perception of fatigue in patients with chronic pain? Findings from studies for management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain with duloxetine. Pain Pract. 2009;9:354–62.
Doth AH, Hansson PT, Jensen MP, Taylor RS. The burden of neuropathic pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of health utilities. Pain. 2010;149:338–44.
Turk DC, Audette J, Levy RM, Mackey SC, Stanos S. Assessment and treatment of psychosocial comorbidities in patients with neuropathic pain. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85:S42–50.
Haanpää ML, Gourlay GK, Kent JL, Miaskowski C, Raja SN, Schmader KE, et al. Treatment considerations for patients with neuropathic pain and other medical comorbidities. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85:S15–25.
Fishbain DA, Cole B, Lewis JE, Gao J. What is the evidence for chronic pain being etiologically associated with the DSM-IV category of sleep disorder due to a general medical condition? A structured evidence-based review. Pain Med. 2010;11:158–79.
Ritzwoller DP, Ellis JL, Korner EJ, Hartsfield CL, Sadosky A. Comorbidities, healthcare service utilization and costs for patients identified with painful DPN in a managed-care setting. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009;25:1319–28.
DiBonaventura MD, Cappelleri JC, Joshi AV. Association between pain severity and health care resource use, health status, productivity and related costs in painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy patients. Pain Med. 2011;12:799–807.
• Spallone V. Management of painful diabetic neuropathy: guideline guidance or jungle? Curr Diab Rep. 2012;12:403–13. This paper provides a critical evaluation of the guidelines on the management of neuropathic pain.
Lunn MP, Hughes RA, Wiffen PJ. Duloxetine for treating painful neuropathy or chronic pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;7:CD007115.
Moore RA, Straube S, Wiffen PJ, Derry S, McQuay HJ. Pregabalin for acute and chronic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;8:CD007076.
Bouhassira D, Attal N, Alchaar H, Boureau F, Brochet B, Bruxelle J, et al. Comparison of pain syndromes associated with nervous or somatic lesions and development of a new neuropathic pain diagnostic questionnaire (DN4). Pain. 2005;114:29–36.
• Spallone V, Morganti R, D’Amato C, Greco C, Cacciotti L, Marfia GA. Validation of DN4 as a screening tool for neuropathic pain in painful diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabet Med. 2012;29:578–85. This is the first validation study of the screening tool DN4 for painful diabetic polyneuropathy with values of sensitivity and specificity of 80% and 92%, respectively.
Halawa MR, Karawagh A, Zeidan A, Mahmoud AE, Sakr M, Hegazy A. Prevalence of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy among patients suffering from diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010;26:337–43.
• Jambart S, Ammache Z, Haddad F, Younes A, Hassoun A, Abdalla K, et al. Prevalence of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy among patients with diabetes mellitus in the Middle East region. J Int Med Res. 2011;39:366–77. This is a large epidemiological study of painful diabetic neuropathy in the Middle East Region.
Tesfaye S, Chaturvedi N, Eaton SE, Ward JD, Manes C, Ionescu-Tirgoviste C, et al. Vascular risk factors and diabetic neuropathy.EURODIAB Prospective Complications Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:341–50.
Partanen J, Niskanen L, Lehtinen J, Mervaala E, Siitonen O, Uusitupa M. Natural history of peripheral neuropathy in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1995;13:89–94.
Sorensen L, Molyneaux L, Yue DK. Insensate vs painful diabetic neuropathy: the effects of height, gender, ethnicity and glycemic control. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2002;57:45–51.
Sibal L, Law HN, Gebbie J, Home P. Cardiovascular risk factors predicting the development of distal symmetrical polyneuropathy in people with type 1 diabetes: a 9-year follow-up study. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1084:304–18.
Ziegler D, Rathmann W, Dickhaus T, Meisinger C, Mielck A, KORA Study Group. Prevalence of polyneuropathy in pre-diabetes and diabetes is associated with abdominal obesity and macroangiopathy: the MONICA/KORA Augsburg Surveys S2 and S3. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:464–9.
Ziegler D, Rathmann W, Meisinger C, Dickhaus T, Mielck A, KORA Study Group. Prevalence and risk factors of neuropathic pain in survivors of myocardial infarction with pre-diabetes and diabetes. The KORA Myocardial Infarction Registry. Eur J Pain. 2009;13:582–7.
Panero F, Novelli G, Zucco C, Fornengo P, Perotto M, Segre O, et al. Fasting plasma C-peptide and micro- and macrovascular complications in a large clinic-based cohort of type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:301–5.
Pop-Busui R, Roberts L, Pennathur S, Kretzler M, Brosius FC, Feldman EL. The management of diabetic neuropathy in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;55:365–85.
Davis TM, Yeap BB, Davis WA, Bruce DG. Lipid-lowering therapy and peripheral sensory neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: the Fremantle Diabetes Study. Diabetologia. 2008;51:562–6.
Wiggin TD, Sullivan KA, Pop-Busui R, Amato A, Sima AA, Feldman EL. Elevated triglycerides correlate with progression of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes. 2009;58:1634–40.
Sun JK, Keenan HA, Cavallerano JD, Asztalos BF, Schaefer EJ, Sell DR, et al. Protection from retinopathy and other complications in patients with type 1 diabetes of extreme duration: the joslin 50-year medalist study. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:968–74.
Harris M, Eastman R, Cowie C. Symptoms of sensory neuropathy in adults with NIDDM in the U.S. population. Diabetes Care. 1993;16:1446–52.
Spallone V, Morganti R, D’Amato C, Cacciotti L, Fedele T, Maiello MR, et al. Clinical correlates of painful diabetic neuropathy and relationship of neuropathic pain with sensorimotor and autonomic nerve function. Eur J Pain. 2011;15:153–60.
Wu EQ, Borton J, Said G, Le TK, Monz B, Rosilio M, et al. Estimated prevalence of peripheral neuropathy and associated pain in adults with diabetes in France. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007;23:2035–42.
Erbas T, Ertas M, Yucel A, Keskinaslan A, Senocak M, TURNEP Study Group. Prevalence of peripheral neuropathy and painful peripheral neuropathy in Turkish diabetic patients. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2011;28:51–5.
Benbow SJ, Chan AW, Bowsher D, MacFarlane IA, Williams G. A prospective study of painful symptoms, small-fiber function and peripheral vascular disease in chronic painful diabetic neuropathy. Diabet Med. 1994;11:17–21.
Cheng YJ, Gregg EW, Kahn HS, Williams DE, De Rekeneire N, Narayan KM. Peripheral insensate neuropathy-a tall problem for US adults? Am J Epidemiol. 2006;164:873–80.
Smith AG, Russell J, Feldman EL, Goldstein J, Peltier A, Smith S, et al. Lifestyle intervention for pre-diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:1294–9.
Dyck PJ, Klein CJ, Weigand SD. Does impaired glucose metabolism cause polyneuropathy? Review of previous studies and design of a prospective controlled population-based study. Muscle Nerve. 2007;36:536–41.
• Papanas N, Ziegler D. Prediabetic neuropathy: does it exist? Curr Diab Rep. 2012;12:376–83. This paper reviews available findings on epidemiological, clinical, and pathogenetic aspects of peripheral and autonomic prediabetic neuropathy.
Herman RM, Brower JB, Stoddard DG, Casano AR, Targovnik JH, Herman JH, et al. Prevalence of somatic small fiber neuropathy in obesity. Int J Obes. 2007;31:226–35.
Smith AG, Rose K, Singleton JR. Idiopathic neuropathy patients are at high risk for metabolic syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 2008;273:25–8.
Figueroa-Romero C, Sadidi M, Feldman EL. Mechanisms of disease: the oxidative stress theory of diabetic neuropathy. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2008;9:301–14.
Cameron NE, Cotter MA. Pro-inflammatory mechanisms in diabetic neuropathy: focus on the nuclear factor kappa B pathway. Curr Drug Targets. 2008;9:60–7.
Maury E, Brichard SM. Adipokine dysregulation, adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic syndrome. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;314:1–16.
Ohayon MM, Stingl JC. Prevalence and comorbidity of chronic pain in the German general population. J Psychiatr Res. 2012;46:444–50.
Yagihashi S, Yamagishi S, Wada R. Pathology and pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic neuropathy: correlation with clinical signs and symptoms. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;77:S184–9.
Boulton AJM, Armstrong WD, Scarpello JHB, Ward JD. The natural history of painful diabetic neuropathy: a 4-year study. Postgr Med J. 1983;59:556–9.
Galer BS, Gianas A, Jensen MP. Painful diabetic polyneuropathy: epidemiology, pain description, and quality of life. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2000;47:123–8.
Veves A, Manes C, Murray HJ, Young MJ, Boulton AJ. Painful neuropathy and foot ulceration in diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 1993;16:1187–9.
Ward JD. The diabetic leg. Diabetologia. 1982;22:141–7.
Veves A, Young MJ, Manes C, Boulton AJ. Differences in peripheral and autonomic nerve function measurements in painful and painless neuropathy. A clinical study. Diabetes Care. 1994;17:1200–2.
Mondelli M, Aretini A, Baldasseroni A. Distal symmetric polyneuropathy in diabetes. Differences between patients with and without neuropathic pain. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2012;120:45–50.
Krumova EK, Geber C, Westermann A, Maier C. Neuropathic pain: is quantitative sensory testing helpful? Curr Diab Rep. 2012;12:393–402.
Tsigos C, White A, Young RJ. Discrimination between painful and painless diabetic neuropathy based on testing of large somatic nerve and sympathetic nerve function. Diabet Med. 1992;9:359–65.
Krämer HH, Rolke R, Bickel A, Birklein F. Thermal thresholds predict painfulness of diabetic neuropathies. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:2386–91.
Vrethem M, Boivie J, Arnqvist H, Holmgren H, Lindström T. Painful polyneuropathy in patients with and without diabetes: clinical, neurophysiologic, and quantitative sensory characteristics. Clin J Pain. 2002;18:122–7.
• Lauria G, Lombardi R. Small fiber neuropathy: is skin biopsy the holy grail? Curr Diab Rep. 2012;12:384–92. This paper is a comprehensive review on contemporary issues in small fiber neuropathy.
Sorensen L, Molyneaux L, Yue DK. The relationship among pain, sensory loss, and small nerve fibers in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:883–7.
Quattrini C, Tavakoli M, Jeziorska M, Kallinikos P, Tesfaye S, Finnigan J, et al. Surrogate markers of small fiber damage in human diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes. 2007;56:2148–54.
Devigili G, Tugnoli V, Penza P, Camozzi F, Lombardi R, Melli G, et al. The diagnostic criteria for small fiber neuropathy: from symptoms to neuropathology. Brain. 2008;131:1912–25.
Scherens A, Maier C, Haussleiter IS, Schwenkreis P, Vlckova-Moravcova E, Baron R, et al. Painful or painless lower limb dysesthesias are highly predictive of peripheral neuropathy: comparison of different diagnostic modalities. Eur J Pain. 2009;13:711–8.
Said G, Slama G, Selva J. Progressive centripetal degeneration of axons in small fiber diabetic polyneuropathy. Brain. 1983;106:791–807.
Winkler AS, Ejskjaer N, Edmonds M, Watkins PJ. Dissociated sensory loss in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabet Med. 2000;17:457–62.
Jimenez-Cohl P, Grekin C, Leyton C, Vargas C, Villaseca R. Thermal threshold: research study on small fiber dysfunction in distal diabetic polyneuropathy. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2012;6:177–83.
Ziegler D, Mayer P, Gries FA. Evaluation of thermal, pain, and vibration sensation thresholds in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetic patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988;51:1420–4.
Dyck PJ, Dyck PJ, Larson TS, O’Brien PC, Velosa JA. Patterns of quantitative sensation testing of hypoesthesia and hyperalgesia are predictive of diabetic polyneuropathy: a study of 3 cohorts. Diabetes Care. 2000;23:510–7.
Zinman LH, Bril V, Perkins BA. Cooling detection thresholds in the assessment of diabetic sensory polyneuropathy: comparison of CASE IV and Medoc instruments. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1674–9.
Vlckova-Moravcova E, Bednarik J, Belobradkova J, Sommer C. Small-fiber involvement in diabetic patients with neuropathic foot pain. Diabet Med. 2008;25:692–9.
Umapathi T, Tan WL, Loke SC, Soon PC, Tavintharan S, Chan YH. Intraepidermal nerve fiber density as a marker of early diabetic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 2007;35:591–8.
Ragé M, Van Acker N, Knaapen MW, Timmers M, Streffer J, Hermans MP, et al. Asymptomatic small fiber neuropathy in diabetes mellitus: investigations with intraepidermal nerve fiber density, quantitative sensory testing and laser-evoked potentials. J Neurol. 2011;258:1852–64.
Løseth S, Mellgren SI, Jorde R, Lindal S, Stålberg E. Polyneuropathy in type and type 2 diabetes: comparison of nerve conduction studies, thermal perception thresholds and intraepidermal nerve fiber densities. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2010;26:100–6.
Putz Z, Tabák AG, Tóth N, Istenes I, Németh N, Gandhi RA, et al. Noninvasive evaluation of neural impairment in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:181–3.
Bickel A, Butz M, Schmelz M, Handwerker HO, Neundörfer B. Density of sympathetic axons in sural nerve biopsies of neuropathy patients is related to painfulness. Pain. 2000;84:413–9.
Tack CJ, van Gurp PJ, Holmes C, Goldstein DS. Local sympathetic denervation in painful diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes. 2002;51:3545–53.
• Gibbons CH, Freeman R. Treatment-induced diabetic neuropathy: a reversible painful autonomic neuropathy. Ann Neurol. 2010;67:534–41. The largest case series and first detailed analysis of acute neuropathies associated with glycemic control.
Novak V, Freimer ML, Kissel JT, Sahenk Z, Periquet IM, Nash SM, et al. Autonomic impairment in painful neuropathy. Neurology. 2001;56:861–8.
Singer W, Spies JM, McArthur J, et al. Prospective evaluation of somatic and autonomic small fibers in selected autonomic neuropathies. Neurology. 2004;62:612–8.
Young RJ, Zhou YQ, Rodriguez E, Prescott RJ, Ewing DJ, Clarke BF. Variable relationship between peripheral somatic and autonomic neuropathy in patients with different syndromes of diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetes. 1986;35:192–7.
Gandhi RA, Marques JL, Selvarajah D, Emery CJ, Tesfaye S. Painful diabetic neuropathy is associated with greater autonomic dysfunction than painless diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:1585–90.
Chouchou F, Pichot V, Perchet C, Legrain V, Garcia-Larrea L, Roche F, et al. Autonomic pain responses during sleep: a study of heart rate variability. Eur J Pain. 2011;15:554–60.
Spallone V, Morganti R, D’Amato C, Di Gennaro F, Greco C, Cacciotti L, et al. Nondipping is a novel associated disorder of painful diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetologia. 2012;55:S480.
Storella RJ, Shi Y, O’Connor DM, Pharo GH, Abrams JT, Levitt J. Relief of chronic pain may be accompanied by an increase in a measure of heart rate variability. Anesth Analg. 1999;89:448–50.
Bouhassira D, Attal N, Willer JC, Brasseur L. Painful and painless peripheral sensory neuropathies due to HIV infection: a comparison using quantitative sensory evaluation. Pain. 1999;80:265–72.
Britland ST, Young RJ, Sharma AK, Clarke BF. Acute and remitting painful diabetic polyneuropathy: a comparison of peripheral nerve fiber pathology. Pain. 1992;48:361–70.
Thomas PK. Diabetic sensorimotor neuropathy: treatment. In: Gries FA, Cameron NE, Low PA, Ziegler D, editors. Textbook of diabetic neuropathy. Stuttgard: Thieme; 2003. p. 208–11.
Llewelyn JG, Gilbey SG, Thomas PK, King RH, Muddle JR, Watkins PJ. Sural nerve morphometry in diabetic autonomic and painful sensory neuropathy: a clinico pathological study. Brain. 1991;114:867–92.
Malik RA, Veves A, Walker D, Siddique I, Lye RH, Schady W, et al. Sural nerve fiber pathology in diabetic patients with mild neuropathy: relationship to pain, quantitative sensory testing and peripheral nerve electrophysiology. Acta Neuropathol. 2001;101:367–74.
Tavakoli M, Petropoulos IN, Malik RA. Assessing corneal nerve structure and function in diabetic neuropathy. Clin Exp Optom. 2012;95:338–47.
Archer AG, Roberts VC, Watkins PJ. Blood flow patterns in painful diabetic neuropathy. Diabetologia. 1984;27:563–7.
Eaton SE, Harris ND, Ibrahim S, Patel KA, Selmi F, Radatz M, et al. Increased sural nerve epineurial blood flow in human subjects with painful diabetic neuropathy. Diabetologia. 2003;46:934–9.
Malik RA, Tesfaye S, Newrick PG, Walker D, Rajbhandari SM, Siddique I, et al. Sural nerve pathology in diabetic patients with minimal but progressive neuropathy. Diabetologia. 2005;48:578–85.
Tesfaye S, Selvarajah D. Advances in the epidemiology, pathogenesis and management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2012;1:8–14.
Quattrini C, Harris ND, Malik RA, Tesfaye S. Impaired skin microvascular reactivity in painful diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:655–9.
Doupis J, Lyons TE, Wu S, Dinh T, Veves A. Microvascular reactivity and inflammatory cytokines in painful and painless peripheral diabetic neuropathy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:2157–63.
Yuen KC, Baker NR, Rayman G. Treatment of chronic painful diabetic neuropathy with isosorbide dinitrate spray: a double-blind placebo-controlled cross-over study. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:1699–703.
Rayman G, Baker NR, Krishnan ST. Glyceryl trinitrate patches as an alternative to isosorbide dinitrate spray in the treatment of chronic painful diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:2697–8.
Costigan M, Scholz J, Woolf CJ. Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2009;32:1–32.
• Baron R, Binder A, Wasner G. Neuropathic pain: diagnosis, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:807–19. This is a practical review on pathophysiology, diagnosis, sensory profile, and treatment of neuropathic pain.
• Berger JV, Knaepen L, Janssen SP, Jaken RJ, Marcus MA, Joosten EA, et al. Cellular and molecular insights into neuropathy-induced pain hypersensitivity for mechanism-based treatment approaches. Brain Res Rev. 2011;67:282–310. This is an updated complete review of novel experimental treatment approaches to neuropathic pain, mainly acting on the spinal nociceptive network.
Ochoa JL, Campero M, Serra J, Bostock H. Hyperexcitable polymodal and insensitive nociceptors in painful human neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 2005;32:459–72.
Ørstavik K, Namer B, Schmidt R, Schmelz M, Hilliges M, Weidner C, et al. Abnormal function of C-fibers in patients with diabetic neuropathy. J Neurosci. 2006;26:11287–94.
Serra J, Bostock H, Solà R, Aleu J, García E, Cokic B, et al. Microneurographic identification of spontaneous activity in C-nociceptors in neuropathic pain states in humans and rats. Pain. 2012;153:42–55.
Baron R, Tölle TR, Gockel U, Brosz M, Freynhagen R. A cross-sectional cohort survey in 2100 patients with painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia: differences in demographic data and sensory symptoms. Pain. 2009;146:34–40.
Spallone V, Morganti R, Greco C, D’ Amato C, Cacciotti L, Marfia GA. Sensory profiles of neuropathic pain in painful diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetologia. 2011;54:S460.
Cruccu G, Truini A. Sensory profiles: a new strategy for selecting patients in treatment trials for neuropathic pain. Pain. 2009;146:5–6.
Truini A, Biasiotta A, La Cesa S, Di Stefano G, Galeotti F, Petrucci MT, et al. Mechanisms of pain in distal symmetric polyneuropathy: a combined clinical and neurophysiological study. Pain. 2010;150:516–21.
Herder C, Lankisch M, Ziegler D, Rathmann W, Koenig W, Illig T, et al. Subclinical inflammation and diabetic polyneuropathy: MONICA/KORA Survey F3 (Augsburg, Germany). Diabetes Care. 2009;32:680–2.
Myers RR, Campana WM, Shubayev VI. The role of neuroinflammation in neuropathic pain: mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Drug Discov Today. 2006;11:8–20.
• Calvo M, Dawes JM, Bennett DL. The role of the immune system in the generation of neuropathic pain. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11:629–42. This is an interesting review on the experimental and human studies showing a bi-directional signalling between sensory and the immune system in the neuropathic pain generation and maintenance.
Uçeyler N, Rogausch JP, Toyka KV, Sommer C. Differential expression of cytokines in painful and painless neuropathies. Neurology. 2007;69:42–9.
Purwata TE. High TNF-alpha plasma levels and macrophages iNOS and TNF-alpha expression as risk factors for painful diabetic neuropathy. J Pain Res. 2011;4:169–75.
Obrosova IG. Diabetic painful and insensate neuropathy: pathogenesis and potential treatments. Neurotherapeutics. 2009;6:638–47.
Fernyhough P, Calcutt NA. Abnormal calcium homeostasis in peripheral neuropathies. Cell Calcium. 2010;47:130–9.
Stirban A, Tschoepe D, Stratmann B. Shifting the disease management paradigm from glucose: what are the pros? Diabetes Care. 2009;32 Suppl 2:S349–52.
•• Bierhaus A, Fleming T, Stoyanov S, Leffler A, Babes A, Neacsu C, et al. Methylglyoxal modification of Nav1.8 facilitates nociceptive neuron firing and causes hyperalgesia in diabetic neuropathy. Nat Med. 2012;18:926–33. This study shows a mechanism for hyperalgesia based on the glycolytic metabolite methylglyoxal. It introduces a previously undescribed pain mechanism and supports a concept of metabolically driven hyperalgesia in diabetes.
Skapare E, Konrade I, Liepinsh E, Makrecka M, Zvejniece L, Svalbe B, et al. Glyoxalase 1 and glyoxalase 2 activities in blood and neuronal tissue samples from experimental animal models of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Physiol Sci. 2012;62:469–78.
Eaton SE, Harris ND, Rajbhandari SM, Greenwood P, Wilkinson ID, Ward JD, et al. Spinal-cord involvement in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Lancet. 2001;7:35–6.
Selvarajah D, Wilkinson ID, Emery CJ, Harris ND, Shaw PJ, Witte DR, et al. Early involvement of the spinal cord in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:2664–9.
Selvarajah D, Wilkinson ID, Emery CJ, Shaw PJ, Griffiths PD, Gandhi R, et al. Thalamic neuronal dysfunction and chronic sensorimotor distal symmetrical polyneuropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2008;51:2088–92.
Sorensen L, Siddall PJ, Trenell MI, Yue DK. Differences in metabolites in pain-processing brain regions in patients with diabetes and painful neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:980–1.
Selvarajah D, Wilkinson ID, Gandhi R, Griffiths PD, Tesfaye S. Microvascular perfusion abnormalities of the Thalamus in painful but not painless diabetic polyneuropathy: a clue to the pathogenesis of pain in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:718–20.
Cauda F, Sacco K, Duca S, Cocito D, D’Agata F, Geminiani GC, et al. Altered resting state in diabetic neuropathic pain. PLoS One. 2009;4:e4542.
• Selvarajah D, Wilkinson ID, Davies J, Gandhi R, Tesfaye S. Central nervous system involvement in diabetic neuropathy. Curr Diab Rep. 2011;11:310–22. This paper reviews the findings on central mechanisms of neuropathic pain in diabetes.
Fischer TZ, Tan AM, Waxman SG. Thalamic neuron hyperexcitability and enlarged receptive fields in the STZ model of diabetic pain. Brain Res. 2009;1268:154–61.
• Fischer TZ, Waxman SG. Neuropathic pain in diabetes-evidence for a central mechanism. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010;6:462–6. This paper reviews the findings that suggest that thalamic neurons can act as central generators or amplifiers of pain in diabetes.
Goldberg YP, Pimstone SN, Namdari R, Price N, Cohen C, Sherrington RP, et al. Human Mendelian pain disorders: a key to discovery and validation of novel analgesics. Clin Genet. 2012;82:367–73.
Faber CG, Hoeijmakers JG, Ahn HS, Cheng X, Han C, Choi JS, et al. Gain of function Naν1.7 mutations in idiopathic small fiber neuropathy. Ann Neurol. 2012;71:26–39.
Faber CG, Lauria G, Merkies IS, Cheng X, Han C, Ahn HS, et al. Gain-of-function Nav1.8 mutations in painful neuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:19444–9.
Tegeder I, Scheving R, Wittig I, Geisslinger G. SNO-ing at the nociceptive synapse? Pharmacol Rev. 2011;63:366–89.
Tegeder I, Costigan M, Griffin RS, Abele A, Belfer I, Schmidt H, et al. GTP cyclohydrolase and tetrahydrobiopterin regulate pain sensitivity and persistence. Nat Med. 2006;12:1269–77.
Backonja M, Woolf CJ. Future directions in neuropathic pain therapy: closing the translational loop. Oncologist. 2010;2:24–9.
Hotta N, Yasuda K, Sumita Y, Sano T, Kakuta H, Nagashima M, et al. Effects of a novel aldose reductase inhibitor, fidarestat (SNK-860), on vibration perception threshold and subjective symptoms in patients with diabetic polyneuropathy: an open-label pilot study. Clin Drug Investig. 2004;24:671–80.
Sima AA, Calvani M, Mehra M, Amato A. Acetyl-L-Carnitine Study Group. Acetyl-L-carnitine improves pain, nerve regeneration, and vibratory perception in patients with chronic diabetic neuropathy: an analysis of 2 randomized placebo-controlled trials. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:89–94.
Ziegler D, Movsesyan L, Mankovsky B, Gurieva I, Abylaiuly Z, Strokov I. Treatment of symptomatic polyneuropathy with actovegin in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:1479–84.
Ropper AH, Gorson KC, Gooch CL, Weinberg DH, Pieczek A, Ware JH, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor gene transfer for diabetic polyneuropathy: a randomized, double-blinded trial. Ann Neurol. 2009;65:386–93.
Ziegler D, Nowak H, Kempler P, Vargha P, Low PA. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: a meta-analysis. Diabet Med. 2004;21:114–21.
Ziegler D, Ametov A, Barinov A, Dyck PJ, Gurieva I, Low PA, et al. Oral treatment with alpha-lipoic acid improves symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy: the SYDNEY 2 trial. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:2365–70.
Fonseca VA, Lavery LA, Thethi TK, Daoud Y, DeSouza C, Ovalle F, et al. Metanx in type 2 diabetes with peripheral neuropathy: a randomized trial. Am J Med. 2013;126:141–9.
Chan AW, MacFarlane IA, Bowsher D, Wells JC, Bessex C, Griffiths K. Chronic pain in patients with diabetes mellitus: comparison with a non-diabetic population. The Pain Clinic. 1990;3:147–59.
Acknowledgment
Carla Greco is a trainee of the Specialization School for Nutritional Sciences of Tor Vergata University, Rome, Italy.
Conflict of Interest
Vincenza Spallone has board membership with Wörwag Pharma, TRIGOcare International, Daichii Sankyo Europe, and Ely Lilly Italy. She also has been a consultant for AWP srl, Wörwag Pharma Group. She has received grant support from Biocure SrL. She has received payment for development of educational presentations including service on speakers’ bureaus for continuing medical education from Ely Lilly Italy, Sanofi Aventis, and Pfizer Italy.
Carla Greco declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spallone, V., Greco, C. Painful and Painless Diabetic Neuropathy: One Disease or Two?. Curr Diab Rep 13, 533–549 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-013-0387-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-013-0387-7