Abstract
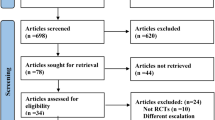
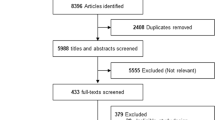
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are increasingly used in patients with type 2 diabetes. However, the effect on abdominal obesity has not yet been confirmed. The study aimed to systematically evaluate the effect of GLP-1RAs on waist circumference in patients with type 2 diabetes. MEDLINE, EMBASE, the Cochrane library and www.clinicaltrialgov were searched through October 31, 2013. Randomized controlled trials with available data were selected if they compared GLP-1 RAs with placebo and traditional anti-diabetic drugs with a duration ≥8 weeks. Weighted mean difference was estimated using random-effect model. Network meta-analysis was performed to supplement direct comparisons. Seventeen trials with 12 treatments were included. Overall, significant reductions on waist circumference following treatment of liraglutide—1.8 mg once daily (−5.24 cm, 95 % CI −7.68, −2.93), liraglutide—1.2 mg once daily (−4.73 cm, 95 % CI −6.68, −2.65) and exenatide—10 μg twice daily (−1.34 cm, 95 % CI −2.00, −0.75) were detected versus placebo. The reduction effect was more evident when compared with insulin and thiazolidinediones (range −1.71 to −8.03 cm). Compared with exenatide, liraglutide—0.6 mg once daily, taspoglutide, liraglutide—1.2 mg once daily and liraglutide—1.8 mg once daily significantly decreased waist circumference from −3.32 to −6.01 cm. Besides, liraglutide—1.8 mg once daily significantly decreased waist circumference by −1.73 cm (95 % CI −3.04, −0.55) versus sitagliptin, whereas no significant difference following liraglutide—1.2-mg-once-daily treatment was detected compared with liraglutide—1.8 mg once daily and sitagliptin. Reduction was observed with statistical significance for exenatide—10 μg twice daily compared with exenatide—5 μg twice daily (−1.21 cm, 95 % CI −2.43, −0.06). Ranking probability analysis indicated liraglutide—1.8 mg once daily and liraglutide—1.2 mg once daily decreased waist circumference most among all 12 treatments with probability of 98.36% and 91.82 %, respectively. Some GLP-1RAs, especially liraglutide—1.8 mg once daily and liraglutide—1.2 mg once daily, were associated with a significant reduction in waist circumference.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.B. Hansen, F.K. Knop, J.J. Holst, T. Vilsbøll, Treatment of type 2 diabetes with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 63, 1154–1160 (2009)
S. Goykhman, A. Drincic, J.C. Desmangles, M. Rendell, Insulin Glargine: A review 8 years after its introduction. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 10, 705–718 (2009)
M.A. Nauck, M.M. Heimesaat, K. Behle, J.J. Holst, M.S. Nauck, R. Ritzel, M. Hüfner, W.H. Schmiegel, Effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 on counter regulatory hormone responses, cognitive functions, and insulin secretion during hyperinsulinemic, stepped hypoglycemic clamp experiments in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 1239–1246 (2002)
T. Vilsbøll, T. Krarup, S. Madsbad, J.J. Holst, Both GLP-l and GIP are insulinotropic at basal and postprandial glucose levels and contribute nearly equally to the incretin effect of a meal in healthy subjects. Regul. Pept. 114, 115–121 (2003)
M. Zander, S. Madsbad, J.L. Madsen, J.J. Holst, Effect of 6-week course of glucagon-like peptide-1 on glycaemic control, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes: A parallel-group study. Lancet 359, 824–830 (2002)
E. Wajcberg, A. Tavaria, Exenaride: clinical aspects of the first incretin-mimetic for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 10, 135–142 (2009)
J.J. Neumiller, R.K. Campbell, Liraglutide: a once-daily incretin mimetic for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann. Pharmacother. 43, 1433–1444 (2009)
C.E. Ezenwaka, O. Okoye, C. Esonwune, P. Onuoha, C. Dioka, C. Osuji, C. Oguejiofor, S. Meludu, High Prevalence of Abdominal Obesity Increases the Risk of the Metabolic Syndrome in Nigerian Type 2 Diabetes Patients: Using the International Diabetes Federation Worldwide Definition. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 12, 277–282 (2014)
R. Bhushan, K.E. Elkind-Hirsch, M. Bhushan, W.J. Butler, K. Duncan, O. Marrioneaux, Improved glycemic control and reduction of cardiometabolic risk factors in subjects with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome treated with exenatide in a clinical practice setting. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 11, 353–359 (2009)
J.A. Beckman, M.A. Creager, P. Libby, Diabetes and atherosclerosis: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA 287, 2570–2581 (2002)
H.M. Lakka, D.E. Laaksonen, T.T. Lakka, The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA 288, 2709–2716 (2002)
P.W. Wilson, R.B. D’Agostino, H. Parise, L. Sullivan, J.B. Meigs, Metabolic syndrome as a precursor of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 112, 3066–3072 (2005)
H. Nagao, S. Kashine, H. Nishizawa, T. Okada, T. Kimura, A. Hirata, S. Fukuda, J. Kozawa, N. Maeda, T. Kitamura, T. Yasuda, K. Okita, T. Hibuse, M. Tsugawa, A. Imagawa, T. Funahashi, I. Shimomura, Vascular complications and changes in body mass index in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients with abdominal obesity. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 12, 88 (2013)
R.R. Wing, B. Marquez, Behavioral aspects of weight loss in type 2 diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 8, 126–131 (2008)
G. Van Valkenhoef, G. Lu, B. de Brock, H. Hillege, A.E. Ades, J. Nicky, Welton Automating network meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 3, 285–299 (2012)
A.R. Jadad, R.A. Moore, D. Carroll, C. Jenkinson, D.J. Reynolds, D.J. Gavaghan, H.J. McQuay, Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control. Clin. Trials 17, 1–12 (1996)
R. DerSimonian, N. Laird, Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 7, 177–188 (1986)
J.P. Higgins, S.G. Thompson, Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 21, 1539–1558 (2002)
G. Lu, A.E. Ades, Combination of direct and indirect evidence in mixed treatment comparisons. Stat. Med. 23, 3105–3124 (2004)
G. Salanti, A.E. Ades, J.P. Ioannidis, Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: an overview and tutorial. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 64, 163–171 (2011)
Spiegelhalter D.J., Best N.G., Carlin B.P., Van Der Linde A.: Bayesian measures of model complexity an fit. J. Royal. Stat. Soci.: Series B (Statistical Methodology) 64, 583–639 (2002)
F. Song, D.G. Altman, A.M. Glenny, J.J. Deeks, Validity of indirect comparison for estimating efficacy of competing interventions: empirical evidence from published meta-analyses. BMJ 326, 472 (2003)
Apovian C.M., Bergenstal R.M., Cuddihy R.M., Qu Y., Lenox S., Lewis M.S., Glass L.C.: Effects of exenatide combined with lifestyle modification in patients with type 2 Diabetes. Am. J. Med. 123, 468.e9–e17 (2010)
J.B. Buse, R.M. Bergenstal, L.C. Glass, C.R. Heilmann, M.S. Lewis, A.Y. Kwan, B.J. Hoogwerf, J. Rosenstock, Use of twice-daily exenatide in Basal insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 154, 103–112 (2011)
M. Diamant, L. Van Gaal, S. Stranks, B. Guerci, L. MacConell, H. Haber, J. Scism-Bacon, M. Trautmann, Safety and efficacy of once-weekly exenatide compared with insulin glargine titrated to target in patients with type 2 diabetes over 84 weeks. Diabetes Care 35, 683–689 (2012)
M. Davies, S. Heller, S. Sreenan, H. Sapin, O. Adetunji, A. Tahbaz, J. Vora, Once-weekly exenatide versus once- or twice-daily insulin detemir: randomized, open-label, clinical trial of efficacy and safety in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with metformin alone or in combination with sulfonylureas. Diabetes Care 36, 1368–1376 (2013)
M.J. Davies, R. Donnelly, A.H. Barnett, S. Jones, C. Nicolay, A. Kilcoyne, Exenatide compared with long-acting insulin to achieve glycaemic control with minimal weight gain in patients with type 2 diabetes: Results of the helping evaluate exenatide in patients with diabetes compared with long-acting insulin (HEELA) study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 11, 1153–1162 (2009)
R.A. DeFronzo, C. Triplitt, Y. Qu, M.S. Lewis, D. Maggs, L.C. Glass, Effects of exenatide plus rosiglitazone on (beta)-cell function and insulin sensitivity in subjects with type 2 diabetes on metformin. Diabetes Care 33, 951–957 (2010)
G. Derosa, I.G. Franzetti, F. Querci, A. Carbone, L. Ciccarelli, M.N. Piccinni, E. Fogari, P. Maffioli, Variation in inflammatory markers and glycemic parameters after 12 months of exenatide plus metformin treatment compared with metformin alone: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Pharmacotherapy 33, 817–826 (2013)
T. Forst, G. Michelson, F. Ratter, M.M. Weber, S. Anders, M. Mitry, B. Wilhelm, A. Pfützner, Addition of liraglutide in patients with Type 2 diabetes well controlled on metformin monotherapy improves several markers of vascular function. Diabet. Med. 29, 1115–1118 (2012)
H. Harder, L. Nielsen, D.T. Tu, A. Astrup, The effect of liraglutide, a long-acting glucagon-like peptide 1 derivative, on glycemic control, body composition, and 24-h energy expenditure in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 27, 1915–1921 (2004)
T. Kadowaki, M. Namba, T. Imaoka, A. Yamamura, W. Goto, M.K. Boardman, H. Sowa, Improved glycemic control and reduced bodyweight with exenatide: A double-blind, randomized, phase 3 study in Japanese patients with suboptimally controlled type 2 diabetes over 24 weeks. J. Diabetes Invest. 2, 210–217 (2011)
C.J. Li, J. Li, Q.M. Zhang, L. Lv, R. Chen, C.F. Lv, P. Yu, D.M. Yu, Efficacy and safety comparison between liraglutide as add-on therapy to insulin and insulin dose-increase in Chinese subjects with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes and abdominal obesity. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 11, 142 (2012)
J. Liutkus, Rosas Guzman J., Norwood P., Pop L., Northrup J., Cao D., Trautmann M.: A placebo-controlled trial of exenatide twice-daily added to thiazolidinediones alone or in combination with metformin. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 12, 1058–1065 (2010)
R. Pratley, M. Nauck, T. Bailey, E. Montanya, R. Cuddihy, S. Filetti, A. Garber, A.B. Thomsen, H. Hartvig, M. Davies, 1860-LIRA-DPP-4 Study Group: One year of liraglutide treatment offers sustained and more effective glycaemic control and weight reduction compared with sitagliptin, both in combination with metformin, in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomised, parallel-group, open-label trial. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 65, 397–407 (2011)
I. Raz, V. Fonseca, M. Kipnes, L. Durrwell, J. Hoekstra, M. Boldrin, R. Balena, Efficacy and safety of taspoglutide monotherapy in drug-naive type 2 diabetic patients after 24 weeks of treatment: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study (T-emerge 1). Diabetes Care 35, 485–487 (2012)
R.R. Henry, S. Mudaliar, L. Kanitra, M. Woloschak, R. Balena, T-Emerge 3 Study Group: Efficacy and safety of taspoglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin plus pioglitazone over 24 weeks: T-emerge 3 trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 97, 2370–2379 (2012)
R.E. Pratley, D. Urosevic, M. Boldrin, R. Balena, T-emerge 6 Study Group: Efficacy and tolerability of taspoglutide versus pioglitazone in subjects with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled with sulphonylurea or sulphonylurea-metformin therapy: A randomized, double-blind study (T-emerge 6). Diabetes Obes. Metab. 15, 234–240 (2013)
P. Hollander, B. Lasko, A.H. Barnett, M. Bengus, L. Kanitra, F.X. Pi-Sunyer, R. Balena, Effects of taspoglutide on glycemic control and body weight in obese patients with type 2 diabetes (T-emerge 7 study). Obesity (Silver Spring) 21, 238–247 (2013)
D. Mundil, A. Cameron-Vendrig, M. Husain, GLP-1 receptor agonists: a clinical perspective on cardiovascular effects. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 9, 95–108 (2012)
D. Lorber, GLP-1 receptor agonists: effects on cardiovascular risk reduction. Cardiovasc. Ther. 31, 238–249 (2013)
M. Buysschaert, V. Preumont, P.R. Oriot, I. Paris, M. Ponchon, D. Scarnière, P. Selvais, UCL Study Group for Exenatide: One-year metabolic outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with exenatide in routine practice. Diabetes Metab. 36, 381–388 (2010)
M.C. Bunck, M. Diamant, B. Eliasson, A. Cornér, R.M. Shaginian, R.J. Heine, M.R. Taskinen, H. Yki-Järvinen, U. Smith, Exenatide affects circulating cardiovascular risk biomarkers independently of changes in body composition. Diabetes Care 33, 1734–1737 (2010)
Y. Matsuzawa, T. Funahashi, T. Nakamura, The concept of metabolic syndrome: contribution of visceral fat accumulation and its molecular mechanism. J Atheroscler. Thromb. 18, 629–639 (2011)
H. Yanai, H. Adachi, H. Hamasaki, Y. Masui, R. Yoshikawa, S. Moriyama, S. Mishima, A. Sako, Effects of 6-month sitagliptin treatment on glucose and lipid metabolism, blood pressure, body weight and renal function in type 2 diabetic patients: a chart-based analysis. J. Clin. Med. Res. 4, 251–258 (2012)
S. Brunton, GLP-1 receptor agonists vs. DPP-4 inhibitors for type 2 diabetes: is one approach more successful or preferable than the other? Int. J. Clin. Pract. 68, 557–567 (2014)
J. Jendle, M.A. Nauck, D.R. Matthews, A. Frid, K. Hermansen, M. Düring, M. Zdravkovic, B.J. Strauss, A.J. Garber, LEAD-2 and LEAD-3 Study Groups: Weight loss with liraglutide, a once-daily human glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue for type 2 diabetes treatment as monotherapy or added to metformin, is primarily as a result of a reduction in fat tissue. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 11, 1163–1172 (2009)
L. van Bloemendaal, J.S. Ten Kulve, S.E. la Fleur, R.G. Ijzerman, M. Diamant, Effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 on appetite and body weight: focus on the CNS. J. Endocrinol. 221, T1–T16 (2014)
Y. Li, T. Perry, M.S. Kindy, B.K. Harvey, D. Tweedie, H.W. Holloway, K. Powers, H. Shen, J.M. Egan, K. Sambamurti, A. Brossi, D.K. Lahiri, M.P. Mattson, B.J. Hoffer, Y. Wang, N.H. Greig, GLP-1 receptor stimulation preserves primary cortical and dopaminergic neurons in cellular and rodent models of stroke and Parkinsonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 1285–1290 (2009)
P.L. McClean, V. Parthsarathy, E. Faivre, C. Holscher, The diabetes drug liraglutide prevents degenerative processes in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 31, 6587–6594 (2011)
D.M. Caldwell, A.E. Ades, J.P. Higgins, Simultaneous comparison of multiple treatments: combining direct and indirect evidence. BMJ 331, 897–900 (2005)
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all cooperating organizations and their staff whose hard work made this study possible. Special thanks to all of the original study authors who promptly and graciously responded to our requests for information.
Funding
This study is funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81302508), Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20120001110015) and the Doctoral Fund of corps (2010JC15) and National Key Technology R&D Program of China (2009BAI82B04).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Feng Sun and Shanshan Wu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, F., Wu, S., Guo, S. et al. Effect of GLP-1 receptor agonists on waist circumference among type 2 diabetes patients: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Endocrine 48, 794–803 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0373-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0373-0