Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) frequently coexist as they share the pathogenic abnormalities of excess adiposity and insulin resistance. Although type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is due to a relative lack of insulin, an increased prevalence of obesity and insulin resistance in this population means that NAFLD also commonly coexists with this condition. Both T2DM and NAFLD are associated with adverse outcomes of the other; T2DM is a risk factor for progressive liver disease and liver-related death in patients with NAFLD, whereas NAFLD may be a marker of cardiovascular risk and mortality in individuals with T2DM. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis—a histological subtype of NAFLD characterized by hepatocyte injury and inflammation—is present in approximately 10% of patients with T2DM and is associated with an increased risk for the development of cirrhosis and liver-related death. Current treatment strategies aim to improve insulin resistance via weight loss and exercise, improve insulin sensitivity by the use of insulin-sensitizing agents (for example, pioglitazone) and reduce oxidative stress by the use of antioxidants, such as vitamin E. Pioglitazone and vitamin E supplementation show the most promise in improving hepatic steatosis and inflammation but have not yet been demonstrated to improve fibrosis, and concern remains regarding the toxicity of long-term use of both of these agents.
Key Points
-
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is present in 50–60% of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and up to 45% of individuals with T1DM
-
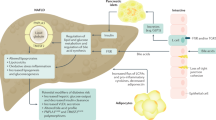
Insulin resistance and NAFLD are closely related: insulin resistance promotes hepatic lipid accumulation and liver injury and hepatic lipid and cytokine release promote hepatic insulin resistance
-
T2DM increases the risk of cirrhosis and liver-related death in patients with NAFLD, whereas NAFLD may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and overall mortality in T2DM
-
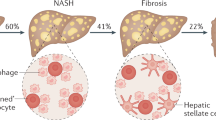
T2DM is a risk factor for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, which is associated with a more aggressive course and higher rates of progression to cirrhosis than simple hepatic steatosis
-
NAFLD is an independent risk factor for the development of cardiovascular disease in patients with T1DM and T2DM
-
For patients with T2DM and NAFLD, weight loss and exercise aim to improve insulin resistance; moreover, insulin-sensitizing agents and antioxidants improve some hepatic parameters, but cardiotoxicity remains a concern
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angulo, P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 346, 1221–1231 (2002).
Neuschwander-Tetri, B. A. & Caldwell, S. H. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: summary of an AASLD Single Topic Conference. Hepatology 37, 1202–1219 (2003).
Rafiq, N. et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 7, 234–238 (2009).
de Marco, R. et al. Cause-specific mortality in type 2 diabetes. The Verona Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 22, 756–761 (1999).
Shaw, J. E., Sicree, R. A. & Zimmet, P. Z. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 87, 4–14 (2010).
Ludwig, J., Viggiano, T. R., McGill, D. B. & Oh, B. J. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 55, 434–438 (1980).
Schaffner, F. & Thaler, H. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Prog. Liver Dis. 8, 283–298 (1986).
Clark, J. M., Brancati, F. L. & Diehl, A. M. The prevalence and etiology of elevated aminotransferase levels in the United States. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 98, 960–967 (2003).
Browning, J. D. et al. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology 40, 1387–1395 (2004).
Fan, J. G. et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for fatty liver in a general population of Shanghai, China. J. Hepatol. 43, 508–514 (2005).
Jimba, S. et al. Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its association with impaired glucose metabolism in Japanese adults. Diabet. Med. 22, 1141–1145 (2005).
Nomura, H., Hayashi, J., Kajiyama, W. & Kashiwagi, S. Prevalence of liver abnormalities in the general population of Okinawa, Japan. Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi 88, 345–351 (1997).
Bedogni, G. et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the Dionysos nutrition and liver study. Hepatology 42, 44–52 (2005).
Schwimmer, J. B. et al. Prevalence of fatty liver in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 118, 1388–1393 (2006).
Marchesini, G. et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver, steatohepatitis, and the metabolic syndrome. Hepatology 37, 917–923 (2003).
Powell, E. E. et al. The natural history of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a follow-up study of forty-two patients for up to 21 years. Hepatology 11, 74–80 (1990).
Bacon, B. R., Farahvash, M. J., Janney, C. G. & Neuschwander-Tetri, B. A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: an expanded clinical entity. Gastroenterology 107, 1103–1109 (1994).
Baldridge, A. D., Perez-Atayde, A. R., Graeme-Cook, F., Higgins, L. & Lavine, J. E. Idiopathic steatohepatitis in childhood: a multicenter retrospective study. J. Pediatr. 127, 700–704 (1995).
Angulo, P., Keach, J. C., Batts, K. P. & Lindor, K. D. Independent predictors of liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 30, 1356–1362 (1999).
Knobler, H. et al. Fatty liver—an additional and treatable feature of the insulin resistance syndrome. QJM 92, 73–79 (1999).
Rashid, M. & Roberts, E. A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 30, 48–53 (2000).
Beymer, C. et al. Prevalence and predictors of asymptomatic liver disease in patients undergoing gastric bypass surgery. Arch. Surg. 138, 1240–1244 (2003).
Gholam, P. M., Flancbaum, L., Machan, J. T., Charney, D. A. & Kotler, D. P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in severely obese subjects. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 102, 399–408 (2007).
Machado, M., Marques-Vidal, P. & Cortez-Pinto, H. Hepatic histology in obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery. J. Hepatol. 45, 600–606 (2006).
Gupte, P. et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 19, 854–858 (2004).
Sanyal, A. J. et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: association of insulin resistance and mitochondrial abnormalities. Gastroenterology 120, 1183–1192 (2001).
Jacqueminet, S. et al. Screening for liver fibrosis by using a noninvasive biomarker in patients with diabetes. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 6, 828–831 (2008).
Porepa, L., Ray, J. G., Sanchez-Romeu, P. & Booth, G. L. Newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for serious liver disease. CMAJ 182, E526–E531 (2010).
Toledo, F. G., Sniderman, A. D. & Kelley, D. E. Influence of hepatic steatosis (fatty liver) on severity and composition of dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 29, 1845–1850 (2006).
Kelley, D. E., McKolanis, T. M., Hegazi, R. A., Kuller, L. H. & Kalhan, S. C. Fatty liver in type 2 diabetes mellitus: relation to regional adiposity, fatty acids, and insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 285, E906–E916 (2003).
Banerji, M. A. et al. Liver fat, serum triglycerides and visceral adipose tissue in insulin-sensitive and insulin-resistant black men with NIDDM. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 19, 846–850 (1995).
Adams, L. A. et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease increases risk of death among patients with diabetes: a community-based cohort study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 105, 1567–1573 (2010).
Wanless, I. R. & Lentz, J. S. Fatty liver hepatitis (steatohepatitis) and obesity: an autopsy study with analysis of risk factors. Hepatology 12, 1106–1110 (1990).
Younossi, Z. M., Gramlich, T., Matteoni, C. A., Boparai, N. & McCullough, A. J. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2, 262–265 (2004).
Ratziu, V. et al. Liver fibrosis in overweight patients. Gastroenterology 118, 1117–1123 (2000).
Adams, L. A., Sanderson, S., Lindor, K. D. & Angulo, P. The histological course of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a longitudinal study of 103 patients with sequential liver biopsies. J. Hepatol. 42, 132–138 (2005).
Matteoni, C. A. et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a spectrum of clinical and pathological severity. Gastroenterology 116, 1413–1419 (1999).
Dam-Larsen, S. et al. Long term prognosis of fatty liver: risk of chronic liver disease and death. Gut 53, 750–755 (2004).
Targher, G., Day, C. P. & Bonora, E. Risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 363, 1341–1350 (2010).
Targher, G. et al. Increased prevalence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetic patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabet. Med. 23, 403–409 (2006).
Targher, G. et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with carotid artery wall thickness in diet-controlled type 2 diabetic patients. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 29, 55–60 (2006).
Targher, G. et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of future cardiovascular events among type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes 54, 3541–3546 (2005).
Targher, G. et al. Non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis and its relation to increased plasma biomarkers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in non-diabetic men. Role of visceral adipose tissue. Diabet. Med. 22, 1354–1358 (2005).
Lautamäki, R. et al. Liver steatosis coexists with myocardial insulin resistance and coronary dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 291, E282–E290 (2006).
Kilpatrick, E. S., Rigby, A. S. & Atkin, S. L. Insulin resistance, the metabolic syndrome, and complication risk in type 1 diabetes: “double diabetes” in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Care 30, 707–712 (2007).
Manton, N. D. et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in children and adolescents. Med. J. Aust. 173, 476–479 (2000).
Leeds, J. S. et al. Abnormal liver function tests in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: prevalence, clinical correlations and underlying pathologies. Diabet. Med. 26, 1235–1241 (2009).
Targher, G. et al. Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its association with cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. J. Hepatol. 53, 713–718 (2010).
Torbenson, M. et al. Glycogenic hepatopathy: an underrecognized hepatic complication of diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 30, 508–513 (2006).
Struben, V. M., Hespenheide, E. E. & Caldwell, S. H. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and cryptogenic cirrhosis within kindreds. Am. J. Med. 108, 9–13 (2000).
Guerrero, R., Vega, G. L., Grundy, S. M. & Browning, J. D. Ethnic differences in hepatic steatosis: an insulin resistance paradox? Hepatology 49, 791–801 (2009).
Weston, S. R. et al. Racial and ethnic distribution of nonalcoholic fatty liver in persons with newly diagnosed chronic liver disease. Hepatology 41, 372–379 (2005).
Riquelme, A. et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its association with obesity, insulin resistance and increased serum levels of C-reactive protein in Hispanics. Liver Int. 29, 82–88 (2009).
Mohanty, S. R. et al. Influence of ethnicity on histological differences in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 50, 797–804 (2009).
Speliotes, E. K. Genetics of common obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 136, 1492–1495 (2009).
Schwimmer, J. B. et al. Heritability of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 136, 1585–1592 (2009).
Wagenknecht, L. E. et al. Correlates and heritability of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a minority cohort. Obesity (Silver Spring) 17, 1240–1246 (2009).
Romeo, S., Huang-Doran, I., Baroni, M. G. & Kotronen, A. Unravelling the pathogenesis of fatty liver disease: patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3 protein. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 21, 247–252 (2010).
Romeo, S. et al. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 40, 1461–1465 (2008).
Valenti, L. et al. Homozygosity for the patatin-like phospholipase-3/adiponutrin I148M polymorphism influences liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 51, 1209–1217 (2010).
Day, C. P. Genetic and environmental susceptibility to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Dis. 28, 255–260 (2010).
Petersen, K. F. et al. Apolipoprotein C3 gene variants in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 362, 1082–1089 (2010).
Adams, L. A., Angulo, P. & Lindor, K. D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. CMAJ 172, 899–905 (2005).
Browning, J. D. & Horton, J. D. Molecular mediators of hepatic steatosis and liver injury. J. Clin. Invest. 114, 147–152 (2004).
Charlton, M., Sreekumar, R., Rasmussen, D., Lindor, K. & Nair, K. S. Apolipoprotein synthesis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 35, 898–904 (2002).
Neuschwander-Tetri, B. A. Hepatic lipotoxicity and the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: the central role of nontriglyceride fatty acid metabolites. Hepatology 52, 774–788 (2010).
Alkhouri, N., Dixon, L. J. & Feldstein, A. E. Lipotoxicity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: not all lipids are created equal. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 3, 445–451 (2009).
Monetti, M. et al. Dissociation of hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance in mice overexpressing DGAT in the liver. Cell. Metab. 6, 69–78 (2007).
Li, Z. Z., Berk, M., McIntyre, T. M. & Feldstein, A. E. Hepatic lipid partitioning and liver damage in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: role of stearoyl-CoA desaturase. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 5637–5644 (2009).
Jaeschke, A. & Davis, R. J. Metabolic stress signaling mediated by mixed-lineage kinases. Mol. Cell 27, 498–508 (2007).
Hotamisligil, G. S. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 444, 860–867 (2006).
Aguirre, V., Uchida, T., Yenush, L., Davis, R. & White, M. F. The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307). J. Biol. Chem. 275, 9047–9054 (2000).
Weston, C. R. & Davis, R. J. The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 19, 142–149 (2007).
Sabio, G. et al. A stress signaling pathway in adipose tissue regulates hepatic insulin resistance. Science 322, 1539–1543 (2008).
Solinas, G. et al. JNK1 in hematopoietically derived cells contributes to diet-induced inflammation and insulin resistance without affecting obesity. Cell. Metab. 6, 386–397 (2007).
Hirosumi, J. et al. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 420, 333–336 (2002).
Schattenberg, J. M., Wang, Y., Singh, R., Rigoli, R. M. & Czaja, M. J. Hepatocyte CYP2E1 overexpression and steatohepatitis lead to impaired hepatic insulin signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 9887–9894 (2005).
Wieckowska, A. et al. Increased hepatic and circulating interleukin-6 levels in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 103, 1372–1379 (2008).
Senn, J. J. et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 (SOCS-3), a potential mediator of interleukin-6-dependent insulin resistance in hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 13740–13746 (2003).
Cai, D. et al. Local and systemic insulin resistance resulting from hepatic activation of IKK-beta and NF-kappaB. Nat. Med. 11, 183–190 (2005).
van der Poorten, D. et al. Visceral fat: a key mediator of steatohepatitis in metabolic liver disease. Hepatology 48, 449–457 (2008).
Ibrahim, M. M. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: structural and functional differences. Obes. Rev. 11, 11–18 (2010).
Weisberg, S. P. et al. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Invest. 112, 1796–1808 (2003).
Shoelson, S. E., Lee, J. & Goldfine, A. B. Inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 1793–1801 (2006).
Wellen, K. E. & Hotamisligil, G. S. Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 1111–1119 (2005).
Hui, J. M. et al. Beyond insulin resistance in NASH: TNF-alpha or adiponectin? Hepatology 40, 46–54 (2004).
Leclercq, I. A., Farrell, G. C., Schriemer, R. & Robertson, G. R. Leptin is essential for the hepatic fibrogenic response to chronic liver injury. J. Hepatol. 37, 206–213 (2002).
Anania, F. A. Leptin, liver, and obese mice—fibrosis in the fat lane. Hepatology 36, 246–248 (2002).
Feldstein, A. E. et al. Free fatty acids promote hepatic lipotoxicity by stimulating TNF-alpha expression via a lysosomal pathway. Hepatology 40, 185–194 (2004).
Haque, M. & Sanyal, A. J. The metabolic abnormalities associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 16, 709–731 (2002).
Paradis, V. et al. High glucose and hyperinsulinemia stimulate connective tissue growth factor expression: a potential mechanism involved in progression to fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 34, 738–744 (2001).
Sugimoto, R. et al. High glucose stimulates hepatic stellate cells to proliferate and to produce collagen through free radical production and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Liver Int. 25, 1018–1026 (2005).
Saadeh, S. et al. The utility of radiological imaging in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 123, 745–750 (2002).
Van Ness, M. M. & Diehl, A. M. Is liver biopsy useful in the evaluation of patients with chronically elevated liver enzymes? Ann. Intern. Med. 111, 473–478 (1989).
Torres, D. M. & Harrison, S. A. Diagnosis and therapy of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 134, 1682–1698 (2008).
Fracanzani, A. L. et al. Risk of severe liver disease in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with normal aminotransferase levels: a role for insulin resistance and diabetes. Hepatology 48, 792–798 (2008).
Harrison, S. A. & Neuschwander-Tetri, B. A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin. Liver Dis. 8, 861–879 (2004).
Yun, J. W. et al. Abnormal glucose tolerance in young male patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 29, 525–529 (2009).
Palmentieri, B. et al. The role of bright liver echo pattern on ultrasound B-mode examination in the diagnosis of liver steatosis. Dig. Liver Dis. 38, 485–489 (2006).
Hamaguchi, M. et al. The severity of ultrasonographic findings in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease reflects the metabolic syndrome and visceral fat accumulation. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 102, 2708–2715 (2007).
Mottin, C. C. et al. The role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of hepatic steatosis in morbidly obese patients. Obes. Surg. 14, 635–637 (2004).
Mazhar, S. M., Shiehmorteza, M. & Sirlin, C. B. Noninvasive assessment of hepatic steatosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 7, 135–140 (2009).
Fishbein, M. H., Gardner, K. G., Potter, C. J., Schmalbrock, P. & Smith, M. A. Introduction of fast MR imaging in the assessment of hepatic steatosis. Magn. Reson. Imaging 15, 287–293 (1997).
Charatcharoenwitthaya, P. & Lindor, K. D. Role of radiologic modalities in the management of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin. Liver Dis. 11, 37–54 (2007).
Szczepaniak, L. S. et al. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy to measure hepatic triglyceride content: prevalence of hepatic steatosis in the general population. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 288, E462–E468 (2005).
Roldan-Valadez, E. et al. In vivo 3T spectroscopic quantification of liver fat content in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Correlation with biochemical method and morphometry. J. Hepatol. 53, 732–737 (2010).
Brunt, E. M., Janney, C. G., Di Bisceglie, A. M., Neuschwander-Tetri, B. A. & Bacon, B. R. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 94, 2467–2474 (1999).
Adams, L. A. et al. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology 129, 113–121 (2005).
Harrison, S. A., Brunt, E. M., Goodman, Z. D. & Di Bisceglie, A. M. Diabetic hepatosclerosis: diabetic microangiopathy of the liver. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 130, 27–32 (2006).
McPherson, S., Stewart, S. F., Henderson, E., Burt, A. D. & Day, C. P. Simple non-invasive fibrosis scoring systems can reliably exclude advanced fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 59, 1265–1269 (2010).
Guha, I. N. et al. Noninvasive markers of fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Validating the European Liver Fibrosis Panel and exploring simple markers. Hepatology 47, 455–460 (2008).
Wong, V. W. et al. Diagnosis of fibrosis and cirrhosis using liver stiffness measurement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 51, 454–462 (2010).
Ratziu, V., Bellentani, S., Cortez-Pinto, H., Day, C. & Marchesini, G. A position statement on NAFLD/NASH based on the EASL 2009 special conference. J. Hepatol. 53, 372–384 (2010).
Juurinen, L., Tiikkainen, M., Häkkinen, A. M., Hakkarainen, A. & Yki-Järvinen, H. Effects of insulin therapy on liver fat content and hepatic insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 292, E829–E835 (2007).
Johnson, N. A. & George, J. Fitness versus fatness: moving beyond weight loss in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 52, 370–381 (2010).
Larson-Meyer, D. E. et al. Effect of calorie restriction with or without exercise on insulin sensitivity, beta-cell function, fat cell size, and ectopic lipid in overweight subjects. Diabetes Care 29, 1337–1344 (2006).
Petersen, K. F. et al. Reversal of nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis, hepatic insulin resistance, and hyperglycemia by moderate weight reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 54, 603–608 (2005).
Tamura, Y. et al. Effects of diet and exercise on muscle and liver intracellular lipid contents and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90, 3191–3196 (2005).
Huang, M. A. et al. One-year intense nutritional counseling results in histological improvement in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a pilot study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 100, 1072–1081 (2005).
Promrat, K. et al. Randomized controlled trial testing the effects of weight loss on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 51, 121–129 (2010).
Harrison, S. A., Fecht, W., Brunt, E. M. & Neuschwander-Tetri, B. A. Orlistat for overweight subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized, prospective trial. Hepatology 49, 80–86 (2009).
St George, A. et al. Independent effects of physical activity in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 50, 68–76 (2009).
Sjöström, L. et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. N. Engl. J. Med. 357, 741–752 (2007).
Chavez-Tapia, N. C. et al. Bariatric surgery for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in obese patients. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Issue 1. Art. No.: CD007340. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007340.pub2 (2010).
Selvin, E. et al. Cardiovascular outcomes in trials of oral diabetes medications: a systematic review. Arch. Intern. Med. 168, 2070–2080 (2008).
Musso, G., Gambino, R., Cassader, M. & Pagano, G. A meta-analysis of randomized trials for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 52, 79–104 (2010).
Aithal, G. P. et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in nondiabetic subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 135, 1176–1184 (2008).
Belfort, R. et al. A placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 355, 2297–2307 (2006).
Sanyal, A. J. et al. Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 362, 1675–1685 (2010).
Ratziu, V. et al. Rosiglitazone for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: one-year results of the randomized placebo-controlled Fatty Liver Improvement with Rosiglitazone Therapy (FLIRT) Trial. Gastroenterology 135, 100–110 (2008).
Omer, Z. et al. Efficacy of insulin-sensitizing agents in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 22, 18–23 (2010).
Nissen, S. E. & Wolski, K. Effect of rosiglitazone on the risk of myocardial infarction and death from cardiovascular causes. N. Engl. J. Med. 356, 2457–2471 (2007).
Adams, L. A. & Angulo, P. Treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Postgrad. Med. J. 82, 315–322 (2006).
Guallar, E., Hanley, D. F. & Miller E. R. 3rd. An editorial update: Annus horribilis for vitamin E. Ann. Intern. Med. 143, 143–145 (2005).
Lindor, K. D. et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid for treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: results of a randomized trial. Hepatology 39, 770–778 (2004).
Leuschner, U. F. et al. High-dose ursodeoxycholic acid therapy for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Hepatology 52, 472–479 (2010).
Abdelmalek, M. F. et al. Betaine for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: results of a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Hepatology 50, 1818–1826 (2009).
Malaguarnera, M. et al. L-carnitine supplementation to diet: a new tool in treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis—a randomized and controlled clinical trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 105, 1338–1345 (2010).
Georgescu, E. F., Ionescu, R., Niculescu, M., Mogoanta, L. & Vancica, L. Angiotensin-receptor blockers as therapy for mild-to-moderate hypertension-associated non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 15, 942–954 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors researched data for the article, provided substantial contributions to discussions of the content, wrote the article and reviewed and/or edited the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, B., Adams, L. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes mellitus: pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol 7, 456–465 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2011.72
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2011.72
This article is cited by
-
Dillenia indica fruit extract alleviates sucrose-induced fatty liver and improves serum biochemical alterations in mice
Nutrire (2023)
-
Fatty liver index as a predictor for incident type 2 diabetes in community-dwelling adults: longitudinal findings over 12 years
Cardiovascular Diabetology (2022)
-
Adipose-derived stem cells alleviate liver injury induced by type 1 diabetes mellitus by inhibiting mitochondrial stress and attenuating inflammation
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2022)
-
In vitro toxic interaction of arsenic and hyperglycemia in mitochondria: an important implication of increased vulnerability in pre-diabetics
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2022)
-
Role of swimming on muscle PGC-1α, FNDC5 mRNA, and assessment of serum omentin, adropin, and irisin in high carbohydrate high fat (HCHF) diet induced obesity in rats
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2020)