Abstract
Objective: To investigate the relationships between resting metabolic rate (RMR) and respiratory exchange ratio (RER) and subsequent changes in body size and fatness.
Design: Prospective longitudinal observational study.
Participants: A sample of 147 participants (76 males, 71 females) 18–68 y of age were followed for approximately 5½ y.
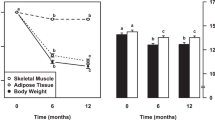
Measures: At baseline, post-absorptive RMR and RER were determined by indirect calorimetry and adjusted for the effects of age, body mass and subcutaneous fatness using regression procedures. Indicators of body size and fatness included body mass, waist circumference, and the sum of six skinfolds. Changes in these indicators (delta scores) were adjusted for age and length of the follow-up period using regression.
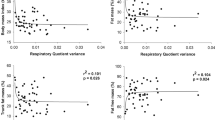
Results: Correlations between baseline RMR, RER and subsequent changes in the indicators of body fatness were uniformly low and not significant (range −0.05–0.16). Further, Cox proportional hazards regression analyses indicated that neither RMR nor RER were significant predictors of gains in body mass, waist circumference, or the sum of six skinfolds.
Conclusions: There is no association between RMR or RER and changes in indicators of body size and fatness over 5½ y of follow-up in this sample.
Sponsorship: This research was supported by The Polar Research Grant on Controlled Heart Rate Zone Exercise from the American College of Sports Medicine Foundation (P.T.K.). The Québec Family Study is currently supported by grants from the Medical Research Council of Canada (PG-11811, GR15187 and MT-13960). C. Bouchard is funded, in part, by the George A. Bray Chair in Nutrition.
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2000) 54, 610–614
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor: Peter T Katzmarzyk.
Contributors: PTK analysed the data and wrote the manuscript; LP aided in interpretation of results and writing of manuscript; AT aided in interpretation of results and writing of manuscript; CB was responsible for design and conception of the study and data collection, he also aided in writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katzmarzyk, P., Pérusse, L., Tremblay, A. et al. No association between resting metabolic rate or respiratory exchange ratio and subsequent changes in body mass and fatness: 5½ year follow-up of the Québec Family Study. Eur J Clin Nutr 54, 610–614 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601053
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601053
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effects of a 12-Week Recreational Soccer Program on Resting Metabolic Rate Among Adolescents with Obesity
Journal of Science in Sport and Exercise (2023)
-
Preoperative high respiratory quotient correlates with lower weight loss after bariatric surgery
Surgical Endoscopy (2020)
-
High respiratory quotient is associated with increases in body weight and fat mass in young adults
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2016)
-
Differences in Daily Energy Expenditure in Lean and Obese Women: The Role of Posture Allocation
Obesity (2008)
-
Ethnic Differences in Body Composition and Other Markers of Cardiovascular Disease Risk: Study in Matched Haitian and White Subjects from Quebec
Obesity (2006)